World’s Richest One Percent Capture Twice as Much Income Growth as the Bottom Half

The inaugural World Inequality Report published on Thursday by economists Thomas Piketty, Emmanuel Saez, Gabriel Zucman, Facundo Alvaredo and Lucas Chancel documents the rise in global income and wealth inequality since 1980.
The report covers up to 2016, leaving out the last year, in which the stock market has soared on the expectation that the US will enact massive tax cuts, providing yet another windfall for the rich.
The report found that between 1980 and 2016 the world’s richest one percent captured twice the income growth as the bottom half of the world’s population, contributing to a significant rise in global inequality.
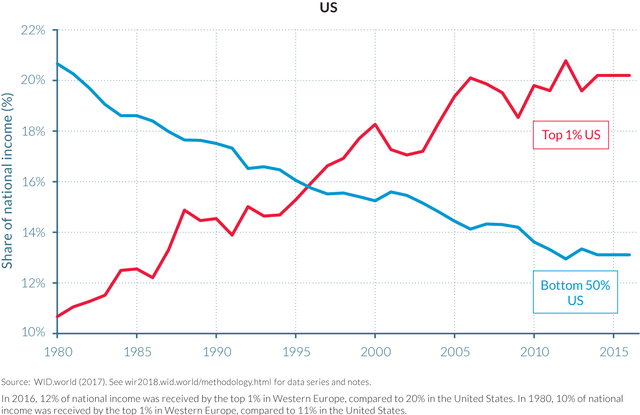
Top 1 percent vs. Bottom 50 percent national income shares in the US 1980–2016
The data shows that the world’s top 0.1 percent alone captured as much growth as the bottom half, and the top 0.001 percent, just 76,000 people worldwide, received 4 percent of global income growth. Meanwhile those in the 50th to 99th percentiles worldwide, which the report refers to as the “squeezed bottom 90 percent in the US and Western Europe,” encompassing the working class in the world’s advanced economies, experienced anemic growth rates.
The report is based on tax data and other financial information collected for the World Wealth and Income Database by more than 100 researchers in 70 countries. It shows that income inequality has either risen or remained stable in every country.
Additionally, the report found that concentration of wealth in the hands of the top one percent has risen sharply, particularly in the US, Russia and China. In the US, the wealth share monopolized by the top one percent rose from 22 percent in 1980 to 39 percent; in China it doubled from 15 percent to 30 percent; and in Russia it went from 22 percent to 43 percent.
In terms of income, the top ten percent captured 37 percent of national income in Europe, 41 percent in China, 47 percent in the United States-Canada, 54 percent in Sub-Saharan Africa, 55 percent in Brazil and India, and 61 percent in the Middle East.
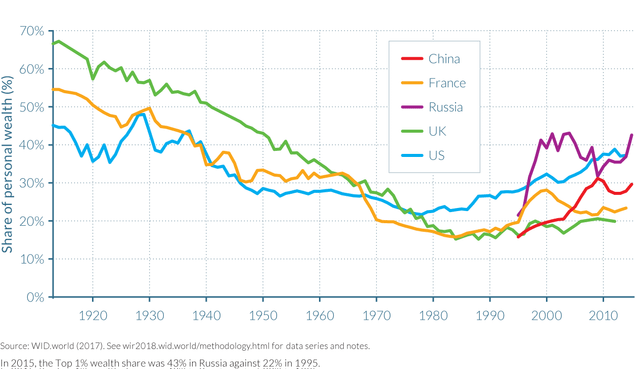
Top 1 percent wealth shares across the world, 1913–2015
Notably, Russia, when it was still part of the Soviet Union, had the lowest level of inequality in 1980, with the top ten percent accounting for 20 percent of income. There was a sharp spike in inequality following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1990-91, with half of all national income going to the top ten percent in less than five years. Russia has now reached parity with the United States, returning to levels of inequality that prevailed a century ago under the rule of the tsar.
The report also shows that there has been a significant divergence in inequality levels between the United States and Europe since 1980, when the top one percent claimed 10 percent of income in both regions. As of 2016, the top one percent in Europe claimed 12 percent of income, while in the United States its share had doubled to 20 percent.
The top one percent and the bottom half of the American population have essentially flipped positions. While the bottom 50 percent received 20 percent of national income in 1980, that figure declined steadily to just 13 percent by 2016. Conversely, the top one percent steadily increased their claim on national income, from 10 percent to 20 percent in less than two generations.
Average annual income for the bottom half of the US population, adjusted for inflation, has remained at $16,500 for the last 40 years, while the top one percent have seen their average income triple from $430,000 to $1.3 million.
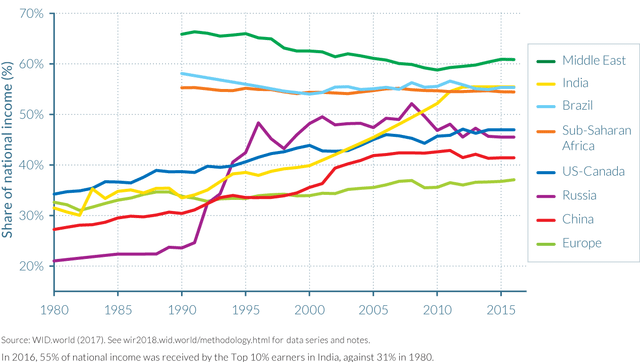
Top 10 percent income shares across the world, 1980–2016
The report’s authors note in an op-ed published in the Guardian that the United States is an outlier among the advanced economies, with a surge in income and wealth inequality over the last four decades that has developed into a “second Gilded Age.”
The authors attribute the dramatic difference between the US and Europe to a “perfect storm of radical policy changes” in the US. They argue that the growth of inequality in the US has been exacerbated by a number of factors, including a tax system that has become less progressive over time, a federal minimum wage that has not kept up with inflation, shrinking unions, deregulation of the finance industry and increasingly unequal access to higher education. They warn that the Republican tax cuts will “turbocharge” the further rise of inequality.
Despite its explosive content, the latest report on inequality was buried by the media, relegated to a small headline in the Business Day section of the New York Times and posted well down the Guardian’s front page in the world news section. The vast and ever-growing level of social inequality around the world is not what the ruling classes in the US, Europe and elsewhere want to talk about.
Social inequality in the United States is being ignored and covered up by the political system. The Democrats are entirely focused on issues of sex and the anti-Russia campaign, even as the Republicans are pushing to finalize tax cuts for corporations and the wealthy by the end of the year.
However, under the surface of official life, class conflict is growing. The World Inequality Report reveals that the contradictions of the capitalist system find expression in every country.
In concluding their report, the authors refer to policy decisions that could be adopted to reverse the growth of social inequality, promoting the illusion that a fair distribution of resources can be achieved under capitalism through various liberal reform measures and appeals to capitalist governments to enact progressive tax measures.
There is, however, no “reform” faction in the ruling class. The growth of inequality in the US has been carried out under both Democrats and Republicans, aided and abetted by the trade unions. In Europe, the ruling elite is moving rapidly to catch up to the United States through the implementation of labor “reform” measures, the destruction of social programs and the redistribution of wealth to the rich.
The response of the ruling class to growing social opposition is not reform, but repression. A movement against inequality requires the building of a socialist movement of the international working class on the basis of a socialist program to appropriate the wealth of the corporate and financial oligarchy, transform the banks and giant corporations into democratically controlled public utilities, and reorganize economic life on the basis of social need.

