When Corporations Ransack Countries: A Primer on Investor-state Dispute Settlement (ISDS)
“If you wanted to convince the public that international trade agreements are a way to let multinational companies get rich at the expense of ordinary people, this is what you would do: give foreign firms a special right to apply to a secretive tribunal of highly paid corporate lawyers for compensation whenever a government passes a law to, say, discourage smoking, protect the environment or prevent a nuclear catastrophe. Yet that is precisely what thousands of trade and investment treaties over the past half century have done, through a process known as ‘investor-state dispute settlement,’ or ISDS.”
This is how, in autumn 2014, The Economist introduced its readers to a once unknown element in international trade and investment agreements. The business magazine referred to ISDS as “a special privilege that many multinationals have abused”1 and mentioned two infamous examples: Swedish energy giant Vattenfall suing Germany for €6.1 billion2 in damages because the country phased out nuclear power after the Fukushima disaster; and tobacco company Philip Morris suing Uruguay and Australia over government health warnings on cigarette packs and other measures to reduce smoking.
ISDS has morphed from a rarely used last resort… into a powerful tool that corporations brandish ever more frequently, often against broad public policies that they claim crimp profits.
ISDS has morphed from a rarely used last resort… into a powerful tool that corporations brandish ever more frequently, often against broad public policies that they claim crimp profits.
Pulitzer Prize-winning Journalist Chris Hamby3
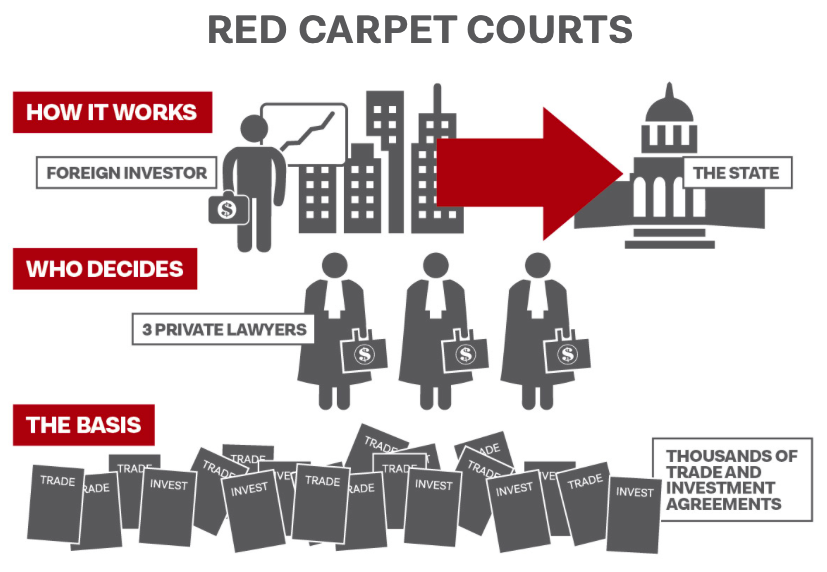
The legal basis for these investor-state dispute settlements – known under the acronym ISDS – is over 2,650 international trade and investment agreements in force between states worldwide.4 These agreements give sweeping powers to foreign investors, including the peculiar privilege to directly file lawsuits against states at international arbitration tribunals. Companies can claim compensation for actions by host governments that have allegedly damaged their investment, either directly through expropriation, for example, or indirectly through virtually any kind of regulation. ‘Investment’ is interpreted so broadly that mere shareholders and rich individuals can sue, and corporations can claim not just for the money invested, but for future anticipated earnings as well.
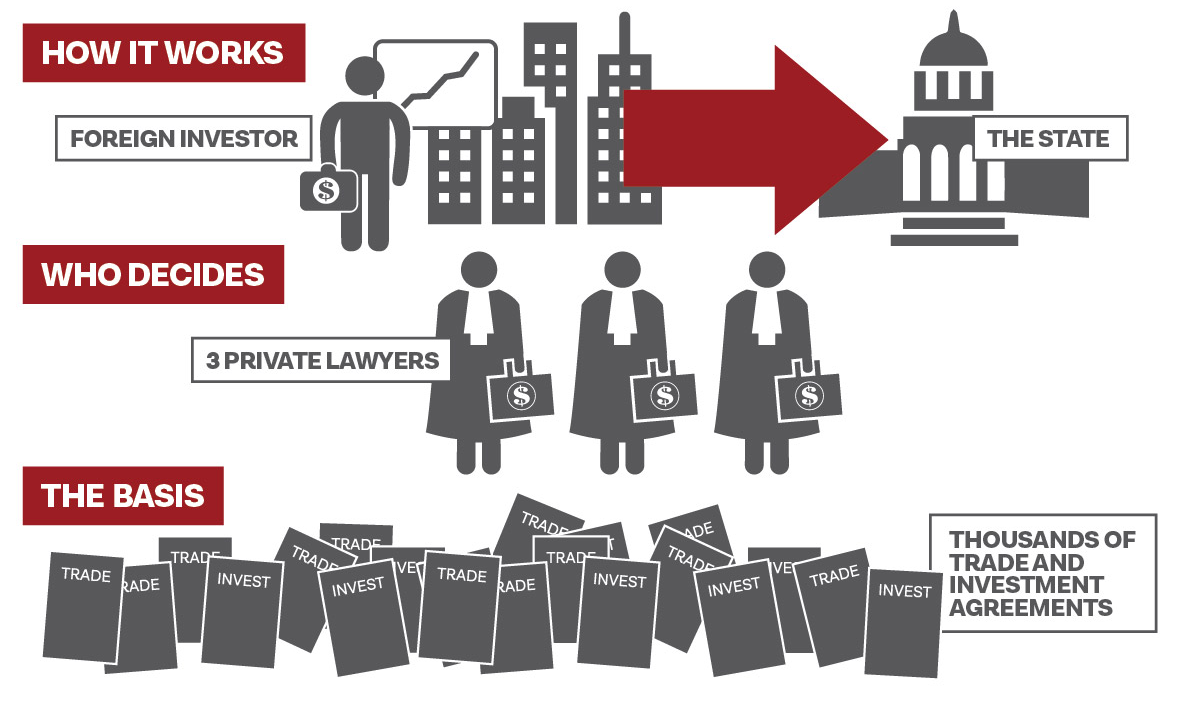
ISDS claims are usually decided by a tribunal of three private lawyers – the arbitrators – who are chosen by the litigating investor and the state. Unlike judges, these for-profit private sector arbitrators do not have a flat salary paid for by the state, but are in fact paid per case. At the most frequently used tribunal, the International Center for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID), arbitrators make US$3,000 a day.5 In a one-sided system where only the investors can bring claims, this clearly creates a strong incentive to side with companies rather than states – because investor-friendly rulings pave the way for more lawsuits and more income in the future.
Read full article on tenissdstories.org here (carefully documented).
*
Note to readers: please click the share buttons above or below. Forward this article to your email lists. Crosspost on your blog site, internet forums. etc.
Featured image is from Flickr