Rockets Destroy Ozone and Cause Climate Change – Aerospace Programs’ Deadly Impacts to the Earth
All Global Research articles can be read in 51 languages by activating the “Translate Website” drop down menu on the top banner of our home page (Desktop version).
To receive Global Research’s Daily Newsletter (selected articles), click here.
Visit and follow us on Instagram at @globalresearch_crg.
***
Since its beginnings, the space industry has used PR, Hollywood, and a parade of stars to carve itself into the public psyche, including targeting children. Aerospace costs have been largely ignored or hidden, but these costs are serious and accelerating.
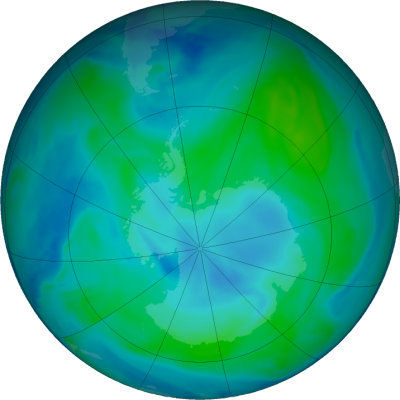
The ozone layer in the sky continues to deteriorate despite international action such as the ban on CFCs. The Antarctic ozone hole is becoming permanent year-round, and the soothing green and blue on NASA’s maps actually signifies low ozone levels.1 The aerospace industry is a major factor in this problem. Dallas etal. (2020): [O]zone depletion is one of the largest environmental concerns surrounding rocket launches from Earth.”2 Why?
1. Rockets’ radical emissions cause immediate, almost total ozone destruction for hundreds of square miles and which lasts days.3
2. Rockets’ exhaust and pollutants introduced into the stratosphere persist there and react with and destroy ozone over the long term.4
3. The sun creates the ozone layer by changing oxygen into ozone in the stratosphere. But rockets put pollutants such as exhaust, water vapor, black carbon, and fuel components such as alumina into the stratosphere, blocking the sun’s rays. This reduces the sun’s creation of ozone, reducing ozone layer repair and replenishment. The long-lived rocket byproducts persist in the stratosphere for 3-5 years,5 and accumulate with every rocket launch, decreasing ozone regeneration with each launch.6
4. The shockwave of de-orbitting debris, satellites, and rockets creates nitric oxide which destroys ozone.7
There is no environmental oversight. Researchers including Martin Ross, Darin Toohey, and James Vedda have repeatedly warned the industry,8 but the industry and governments are escalating space funding and programs instead.
Prior to 2021, 2000 satellites were in orbit around the Earth. Then in 2021, 2800 satellites were launched — more than doubling the total in just one year.9 However, the FCC has approved 17,270 low-earth-orbit (LEO) satellites. 65,912 more LEO applications are pending. Governments and private companies plan an additional 30,947+. Rwanda has applied to the ITU for a staggering 327,320 satellites (Firstenberg, 2022). These numbers don’t include systems fewer than five satellites, geostationary, or medium earth orbit (MEO) satellites, or rockets into space.
These programs will acceleratingly destroy the ozone layer which is essential to protect the Earth and life.10 NASA discovered in 2007 that UV-C and UV-B were already reaching the Earth and failed to act.11 UV radiation is having lethal effects on species now.
LEO satellites are very short-lived, lasting 5-7 years; the U.S. military plans 3-year duration satellites. These LEOs need frequent replacement via rocket launch.
Aleksandr Dunayev of the Russian Space Agency said in 1991: “About 300 launches of the [space] shuttle each year would be a catastrophe, and the ozone layer would be completely destroyed.”12
Science author Arthur Firstenberg says: “In 2021, there were 146 orbital rocket launches to put 1,800 satellites into space. At that rate, to maintain and continually replace 100,000 low-earth-orbit satellites, which have a lifespan of five years, would require more than 1,600 rocket launches per year, or more than four every day, forever into the future.”13 That’s over five times the amount to totally destroy the ozone layer.
The long-lived rocket pollution in the stratosphere also traps Earth’s natural and human-made heat under a rapidly thickening blanket, preventing the heat from venting into space. This will increasingly raise Earth’s temperature.14 This has nothing to do with carbon or methane. However, the increased heat will release methane stored in permafrost and formerly ice-covered regions, and this methane will poison Earth.
These satellite systems are largely intended for 4G/5G global Wi-Fi, military warfighting, and the Internet of Things. They exponentially increase RF-EMF radiation levels in the atmosphere and on Earth. This radiation damages health and causes environmental damage. It damages neurology, DNA, cell membranes, the brain, cognition, learning, memory, immunity, reproduction and fertility, blood, and mitochondria, dysregulates hormones, the blood-brain barrier, and sleep cycles, and causes cancer, stroke, heart attacks, and oxidative stress.15
It disrupts wildlife’s ability to navigate and orient by Earth’s natural EMF fields. Bees, insects, and birds are particularly vulnerable.16 The U.S. Department of Interior warned in 2014 about the devastating impacts to birds from this radiation.17 In 2020, a 5G military/SpaceX “live fire” drill killed up to millions of birds in the Southwest.18 Western governments and the FCC ignore the substantial research showing devastating impacts.
What a disaster.
Another problem: dead spacecraft and debris are rapidly accumulating in the sky, creating collision hazards for other rockets, satellites, and the space stations.19 Every collision creates more debris, leading to more collisions. Unstoppable chain-reaction collisions – Kessler Syndrome — are inevitable. It is increasingly difficult to navigate through these debris fields.
High rates of satellite failure leave dead, unmaneuverable satellites in orbit. The new large constellations will dramatically worsen this problem.20
All of this debris, computers, electronic and chemical waste, radioactive elements, weapons, dead satellites, rocket parts, and dust come down. Aerospace officials and agencies, including the FCC,21 talk nonsense about “disposal” via “safe” de-orbitting and vaporization, as if the waste simply disappears.
The reality is that de-orbitting and vaporization create new problems — exploding burning debris, aerosolizing toxins, metals, paints, fuels, and other chemicals. They fall into the lower atmosphere to pollute the soil, ocean, waters, and air we breathe. “Vaporized” means it explodes into tiny particles and dust.
With these large constellations of short lifespan, increasing failures, and launch rocket debris, a barrage of debris and fall-out and increasing atmospheric dust are just beginning.
All of this debris burns at very hot temperatures as it re-enters the atmosphere, with big and little chunks landing everywhere.22 Exponential increases in fall-out increases the risk for fires, injuries, deaths, and property damage. A large chunk of space debris fell into a Michigan family’s yard and just missed hitting anyone.23 Hot debris fell in Chile last year causing fires.24 A Russian satellite that was supposed to stay in orbit for ten thousand years fell out of orbit this month and possibly landed in the Pacific Ocean.25
In 2020, the FCC proposed an “acceptable” casualty rate of 1 in 10,000 from falling satellites and rockets.26 The FCC also discussed liability and indemnity. However, any liability depends on debris being attributable to a company or government. Otherwise, injured parties would likely have limited or no recourse.
Direct land, air, and ocean pollution from dumping, rocket liftoffs, launch pad runoff and accidents, is another terrible problem.27
No one is discussing this.
The US also wants to put nuclear power into space 28 — reactors in the sky — and awarded a major contract to a team that includes GE, the company which engineered the flawed Fukushima reactors.29 Rockets can explode at launch, malfunction after launch, or fail to reach orbit. This last happened with SNAP 9-A in 1964. As a result, 2.1 pounds of plutonium-238 “vaporized in the atmosphere and spread worldwide… Dr. John Goffman …concluded that the dispersed deadly plutonium-238 was a leading cause of the increase in cancers around the world today.”30 There have been other space nuclear accidents. Officials don’t seem to care.
The militarization of the atmosphere, space, and the moon risk World War III — another problem. 5G in space will control weapons systems on Earth and in the ocean, 31 including military sonar already responsible for killing hundreds of thousands of dolphins, whales, and other marine animals.32 Elon Musk/SpaceX in partnership with the US government has endangered Chinese astronauts by getting too close to their space station.33 Musk is the same man who advocates nuking Mars and saying the U.S. can coup whatever country it wants for rare earth minerals such as lithium.34 The military and its contractors are not guided by responsible, calm leaders. The worst is already happening.
Add to that accelerating plans to exploit, extract, militarize, and privatize the sovereign moon which stabilizes Earth’s rotation and climates, creates the tides, and is essential to all life, as I detailed in my previous article.35 Who’s protecting the moon and the Earth?
Military conquest, profiteering through extraction, mining, tourism, and exploitation are the main goals driving the expenditure of public monies and private investment, not pretty space pictures or neutral, scientific “exploration”. The plutonium ecocide of Saturn by the space industry via the Cassini probe should have been a wakeup call to pull the plug on NASA and the aerospace industry before more planets are destroyed including the Earth.
Subsidizing this industry has caused a brain drain into its high-paying jobs, neglecting and hampering work on Earth’s urgent problems. And the aerospace industry has siphoned off billions in public funds that could fund solutions, while causing expensive environmental problems to be dealt with “later”. The $10 billion dollar Webb telescope is one recent example. Decisionmakers are dashing headlong toward the mirage of a new Gold Rush.
It’s time to strip back the curtain and reveal the protected astronauts, aerospace moguls, and rocket scientists. They are not heroes. They are destroying the Earth. The joy rides of William Shatner and Jeff Bezos were sickening.
Those who want to stop climate change and protect the ozone layer must halt the space programs including space tourism and military programs.
Those who would protect the environment must stop these programs and do it now.
This is common sense. This is about Earth protection. This is about growing up.
Stop the rockets. Defund the space programs. Protect the Earth now.
*
Note to readers: Please click the share buttons above or below. Follow us on Instagram, @crg_globalresearch. Forward this article to your email lists. Crosspost on your blog site, internet forums. etc.
Nina Beety is an investigative writer and public speaker on foreign policy, the environment, and wireless radiation hazards. Her reports for public officials on Smart/AMI utility meters are on her website www.smartmeterharm.org. She lives in California.
She is a regular contributor to Global Research.
Notes
1 https://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/
https://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/monthly/monthly_2022-01_SH.html
https://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/monthly/monthly_2022-01_NH.html
NASA ozone watch
2 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0959652620302560 (abstract)
The environmental impact of emissions from space launches: A comprehensive review, J.A. Dallas, S. Raval, J.P. Alvarez, Gaitan, S. Saydam, A.G. Dempster, Journal of Cleaner Production, May 10, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120209
3 https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14777620902768867#abstract).
Martin Ross , Darin Toohey , Manfred Peinemann & Patrick Ross (2009) Limits on the Space Launch Market Related to Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Astropolitics, 7:1, 50-82, DOI: 10.1080/14777620902768867
The emissions[Four Main Propellant Types] presented in Table 1 cause prompt and deep ozone loss (approaching 100%) in the immediate plume wake, caused by the radical emissions, over areas of hundreds of square miles lasting several days after launch. These stratospheric ‘‘ozone mini-holes’’ have been well observed in situ by high altitude aircraft plume sampling campaigns.
4 ibid.
Beyond the prompt plume wake ozone destruction, second order processing of rocket combustion products occurs during the weeks and months after launch. The plumes are transported and mixed into the global stratosphere and lose their identity as distinct air masses. This intermediate mesoscale phase would be characterized by complex plume-atmosphere interactions among radicals, reservoirs, and sinks. Significant influences from alumina or soot particles are expected, possibly involving the creation of new H2O related particles. The details of this processing will be highly variable according to altitude and even time of day of launch and certainly has a large influence on the steady-state global ozone loss. A few chance observations of aged plumes confirm the importance of the mesoscale processing. No studies have been done on this aspect of rocket emissions. [emphasis added]
https://www.space.com/38884-rocket-exhaust-space-junk-pollution.html
Leonard David (2017) Spaceflight Pollution: How Do Rocket Launches and Space Junk Affect Earth’s Atmosphere?
As NASA and others launch more rockets, effects on Earth remain a mystery, Oct. 8, 2019
5 https://spacenews.com/op-ed-time-to-clear-the-air-about-launch-pollution/
Martin Ross and James Vedda, Time to clear the air about launch pollution, July 3, 2018
Loren Grush, Why it’s time to study how rocket emissions change the atmosphere, May 31, 2018
6 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2013EF000160/abstract
Martin Ross and Patti Sheaffer (2014) Radiative forcing caused by rocket engine emissions, Earth’s Future. January 23, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013EF000160
7 https://www.space.com/6720-space-littering-impact-earths-atmosphere.html
Leonard David (2009) Space Littering Can Impact Earth’s Atmosphere
8 https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14777620902768867#abstract).
Martin Ross , Darin Toohey , Manfred Peinemann & Patrick Ross (2009) Limits
on the Space Launch Market Related to Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Astropolitics, 7:1, 50-82,DOI:10.1080/14777620902768867
https://aerospace.org/sites/default/files/2018-05/RocketEmissions_0.pdf
Martin Ross and James A. Vedda, The Policy and Science of Rocket Emissions, April 2018
9 https://www.cellphonetaskforce.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/441449-Low-Earth-Orbit-Satellites.pdf
441,449 Low Earth Orbit Satellites Operating, Approved and Proposed, Arthur Firstenberg. January 2022
10 https://file.scirp.org/pdf/ACS_2016012714284145.pdf
Anwar, F., Chaudhry, F.N., Nazeer, S., Zaman, N. and Azam, S. (2016) Causes of Ozone Layer Depletion and Its Effects on Human: Review. Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 6, 129-134. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2016.61011
Claudia von Werlhof, The Moment of Truth Has Come! What Now? Threat to Life on Planet Earth; Ozone Dying and the Deadly Ultraviolet Cosmic Radiation, April 25, 2018
12 New York Times, May 14, 1991, cited in http://stopglobalwifi.org/OpenLettertoMedicalOrganizations.html
Global Union Against Radiation Deployment from Space (GUARDS) letter to World Medical Association, February 16, 2016
13 https://www.cellphonetaskforce.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/441449-Low-Earth-Orbit-Satellites.pdf
Arthur Firstenberg, 441,449 Low Earth Orbit Satellites Operating, Approved and Proposed, January 2022
14 https://www.space.com/38884-rocket-exhaust-space-junk-pollution.html
Leonard David (2017) Spaceflight Pollution: How Do Rocket Launches and Space Junk Affect Earth’s Atmosphere?
15 ibid.
www.mdsafetech.org Physicians for Safe Technology
www.bioinitiative.org Bioinitiative Report
www.emfscientist.org EMF Scientist
www.saferemr.com Electromagnetic Health
www.magdahavas.com Dr. Magda Havas, includes archives of Dr. Zorach Glaser
http://stopglobalwifi.org/OpenLettertoMedicalOrganizations.html
Global Union Against Radiation Deployment from Space (GUARDS) letter to World Medical Association, February 16, 2016
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8425056
James C. Lin, Clear Evidence of Cell-Phone RF Radiation Cancer Risk. Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/MMM.2018.2844058
Lin JC. The Significance of Primary Tumors in the NTP Study of Chronic Rat Exposure to Cell Phone Radiation [Health Matters]. IEEE Microwave Magazine. 20(11):18-21. Nov 2019. DOI:10.1109/MMM.2019.2935361.
https://www.saferemr.com/2018/11/NTP-final-reports31.html
Joel Moskowitz, National Toxicology Program analysis
Robert C. Kane, Cellular Telephone Russian Roulette: A Historical and Scientific Perspective, 2001
16 https://kompetenzinitiative.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/ki_beesbirdsandmankind_screen.pdf
Birds, Bees and Mankind: Destroying Nature by Electrosmog, Ulrich Warnke
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-56948-0.pdf
Radio-Frequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure of Western Honey Bees
17 http://www.ntia.doc.gov/files/ntia/us_doi_comments.pdf
Department of Interior, Comments on FirstNet to Department of Commerce, Feb. 7, 2014
18 https://www.investors.com/news/spacex-starlink-impressed-air-force-in-big-live-fire-exercise/
SpaceX Starlink Impresses Air Force Weapons Buyer In Big Live-Fire Exercise
https://www.tesmanian.com/blogs/tesmanian-blog/starlink-airforce
U.S. Air Force Acquisition Chief is impressed by SpaceX Starlink’s performance during Live-Fire exercise
‘Unprecedented’: Birds mysteriously dropping dead across southwestern U.S.
“It’s just terrible,” NMSU biologist Martha Desmond told CNN. “The number is in the six figures. Just by looking at the scope of what we’re seeing, we know this is a very large event, hundreds of thousands and maybe even millions of dead birds, and we’re looking at the higher end of that.”
19 https://digitalcommons.law.uga.edu/gjicl/vol40/iss2/8/
Meghan R. Plantz, Orbital Debris: Out of Space, 40 Ga. J. Int’l & Comp. L. 585 (2012).
https://www.cellphonetaskforce.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/441449-Low-Earth-Orbit-Satellites.pdf
441,449 Low Earth Orbit Satellites Operating, Approved and Proposed, Arthur Firstenberg. January 2022
https://www.space.com/6720-space-littering-impact-earths-atmosphere.html
Leonard David (2009) Space Littering Can Impact Earth’s Atmosphere
www.scientificamerican.com/article/the-risky-rush-for-mega-constellations/
Jonathan O’Callaghan, The risky rush for mega constellations, October 31, 2019
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/JD094iD01p01047
Zolensky, M.E., D.S. McKay and L.A. Kaczor (1989) A ten-fold increase in the abundance of large solid particles in the stratosphere, as measured over the period 1976-1984. The Journal of Geophysical Research, 94, D1, 1047-1056.
Representative chemical, structural, and morphological analyses of the large (>1 μm diameter) solid particles from three impaction collection surfaces have been performed. These collections sampled the stratosphere at approximately 17–19 km in altitude during 1976, 1981, and 1984…This rise in solid particle number density for the stratosphere over the collection period is likely due to the influx of solid rocket exhaust and rocket and satellite debris into the atmosphere in increasingly larger amounts with time. Some of this material is shed from spacecraft during ascent through the atmosphere, but the majority is probably provided during the descent of material from Earth’s growing belt of debris in low Earth orbit.
Arjun Kharpal, Space companies are racing to beam web access to the entire planet. But ‘space junk’ is a big worry, February 16, 2020
www.scientificamerican.com/article/relentless-rise-of-space-junk-threatens-satellites-and-earth/
Jonathan O’Callaghan, SpaceX’s Starlink could cause cascades of space junk, May 13, 2019
www.law360.com/technology/articles/1314044/satellite-cos-want-fcc-to-reconsider-space-junk-rules
Nadia Dreid, Satellite Cos. Want FCC to Reconsider Space Junk Rules, September 28, 2020
“Once in orbit, the debris can move seven times faster than a bullet, according to NASA.”
Jonathan O’Callaghan, The Risky Rush for Mega-Constellations, 2019
“My concern with these big constellations is the [overall] failure rates,” says Glenn Peterson, a senior engineering specialist at the Aerospace Corporation near Los Angeles. “If a satellite fails, they can’t bring it down any more.” In its own filing with the FCC, Amazon was asked to project the potential collision risk of its Project Kuiper constellation if up to 15 percent of its satellites failed, a high but not unfathomablenumber. U.S.-company Iridium Communications, which launched a constellation of 95 satellites into orbit in the 1990s, found that 30 percent of those satellites failed. If 15 percent of Amazon’s satellites failed in orbit, the company has estimated a 17 percent chance that one of them would collide with a piece of space debris—potentially breaking apart to create more space debris and raise overall collision risks.
21 Mitigation of Orbital Debris in the New Space Age, Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, 35 FCC Rcd 4156 (2020). 20-54
https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/FCC-20-54A1.pdf
22 Meghan R. Plantz, Orbital Debris: Out of Space
Example: “…in 1997, parts of a U.S. launch vehicle, including a 450 pound stainless steel propellant tank, ruptured upon impact close to a farmer’s house in Georgetown, Texas. Other parts from the launch vehicle landed around Texas and Oklahoma, such as the titanium helium-pressurized sphere that
landed 100 miles away in Seguin, Texas.
Samsung’s ‘Space Selfie’ satellite made a crash landing on a Michigan couple’s property, 2019
24 https://www.space.com/fireballs-fall-on-chile.html
Falling Fireballs Crashed in Chile Last Week. They Weren’t Meteorites, Experts Say.
26 https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/FCC-20-54A1.pdf
FCC Order and Notice of Proposed Rulemaking 20-54, IV. Section E Casualty Risk Assessment, p. 81-82. including on cumulative risk for constellations of satellites:
“One approach could be a safe harbor similar to some of the concepts described above, wherein a system satisfying a 1 in 10,000, or other risk metric system-wide would satisfy the safe harbor threshold, such that no further analysis of risk would be required We seek comment on this safe harbor approach and a reasonable risk metric for a safe harbor.”
The following section on indemnification is very revealing about companies’ desire to avoid responsibility for damage.
As NASA and others launch more rockets, effects on Earth remain a mystery, Oct. 8, 2019
28 http://space4peace.blogspot.com/2021/02/our-opposition-remains-dangers-of.html
Bruce Gagnon, Our opposition grows: Dangers of launching nukes into space, Global Network Against Weapons and Nuclear Power in Space. Feb. 15, 2021
USNC-Tech team wins contract to develop nuclear thermal propulsion system for NASA
30 http://space4peace.blogspot.com/2021/02/our-opposition-remains-dangers-of.html
31 See Global Network Against Nuclear Weapons and Nuclear Power in Space www.space4peace.org
https://www.investors.com/news/spacex-starlink-impressed-air-force-in-big-live-fire-exercise/
32 https://stop5ginternational.org/smart-ocean-impacts-of-technology-on-marine-life/
China Angry With Elon Musk Over Space Near-Misses
Rainer Shea, “We will coup whoever we want”: U.S. imperialism’s friendly mask slips off. Op-Ed News, July 27, 2020
35 https://www.globalresearch.ca/who-protecting-moon/5712564
Nina Beety, Who’s Protecting the Moon, Global Research. May 15, 2020
Featured image is from NASA Ozone Hole Watch

