Replicon mRNA Vaccine: Japan Approves World’s First Self-Amplifying mRNA Vaccine
New nightmare hits the market. What now? What are the problems? What about shedding?
All Global Research articles can be read in 51 languages by activating the Translate Website button below the author’s name (only available in desktop version).
To receive Global Research’s Daily Newsletter (selected articles), click here.
Click the share button above to email/forward this article to your friends and colleagues. Follow us on Instagram and Twitter and subscribe to our Telegram Channel. Feel free to repost and share widely Global Research articles.
***
New Year Donation Drive: Global Research Is Committed to the “Unspoken Truth”
*
Nov. 27, 2023 – Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Approves CSL and Arcturus Therapeutics’ ARCT-154, the first Self-Amplifying mRNA vaccine approved for COVID in adults
What Are Self-amplifying mRNA Vaccines?
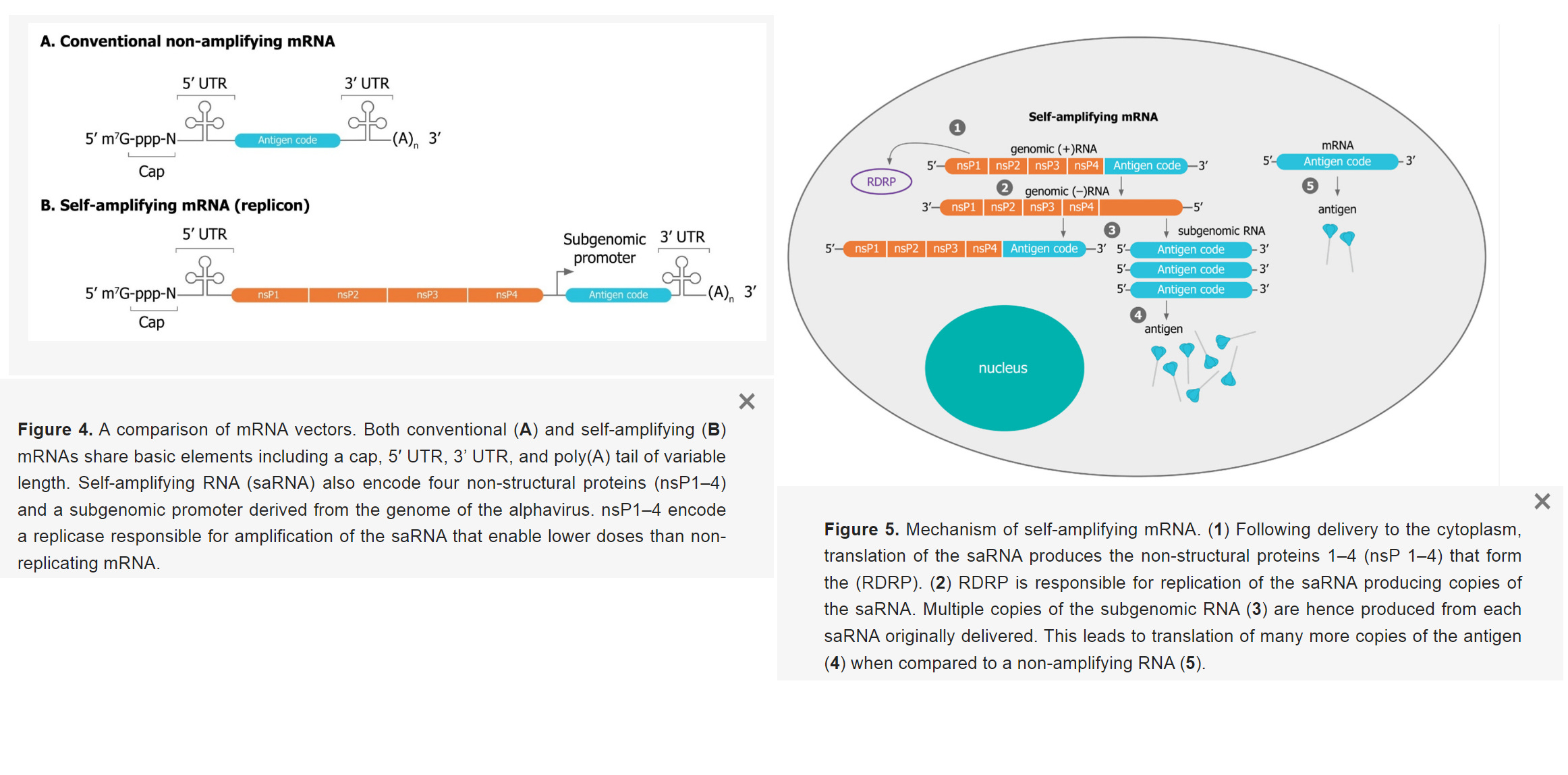
- “Replicons encode their own replication machinery to boost their copy numbers directly after administration in target cells”
- “Replicon RNA additionally encodes viral replicase genes. These genes allow the rapid amplification of the mRNA. The self-amplifying viral genes originated from viruses, for example, alphaviruses and flaviviruses”
The 16 Centre Vietnamese “Safety Study” Japan Government Used for Approval
The Dec. 20, 2023 Japanese Study by Oda, et al
The Dec. 13, 2022 Study by Low, et al
The “Benefits”
The “Problems”
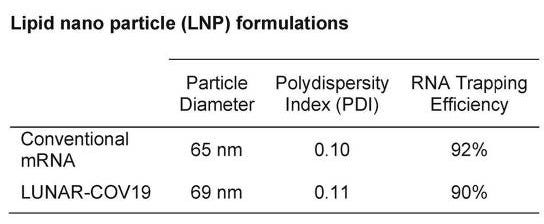
- No safety studies or biodistribution studies available for the Arcturus LNPs.
- sa-mRNA is much larger (due to the additional replication machinery sequences) up to 3 times larger.
- “which leads to challenges during production, such as increased product-related impurities during synthesis and lower binding capacities in chromatography steps due to its larger size.”
- any faulty sa-mRNA once injected, will be amplified in the cell, leading to higher concentrations of faulty proteins.
- most saRNA vaccines are based on the genome of the positive-sensed alphaviruses Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV), Sindbis virus (SINV), or Semliki Forest virus (SFV)(shown below)
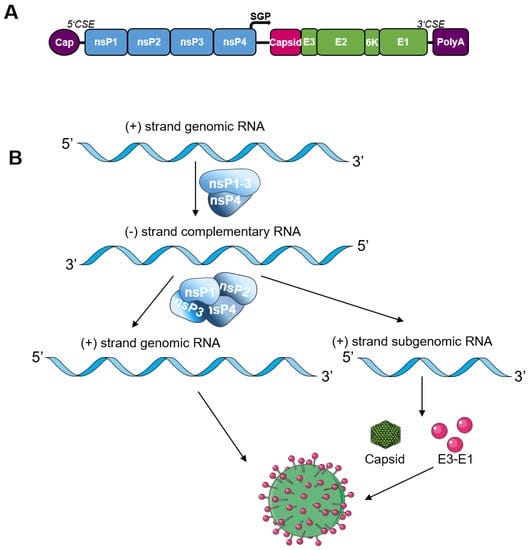
- For the construction of saRNA vaccines, the alphavirus structural proteins are replaced by the antigen gene (spike protein for COVID-19 Vaccines)
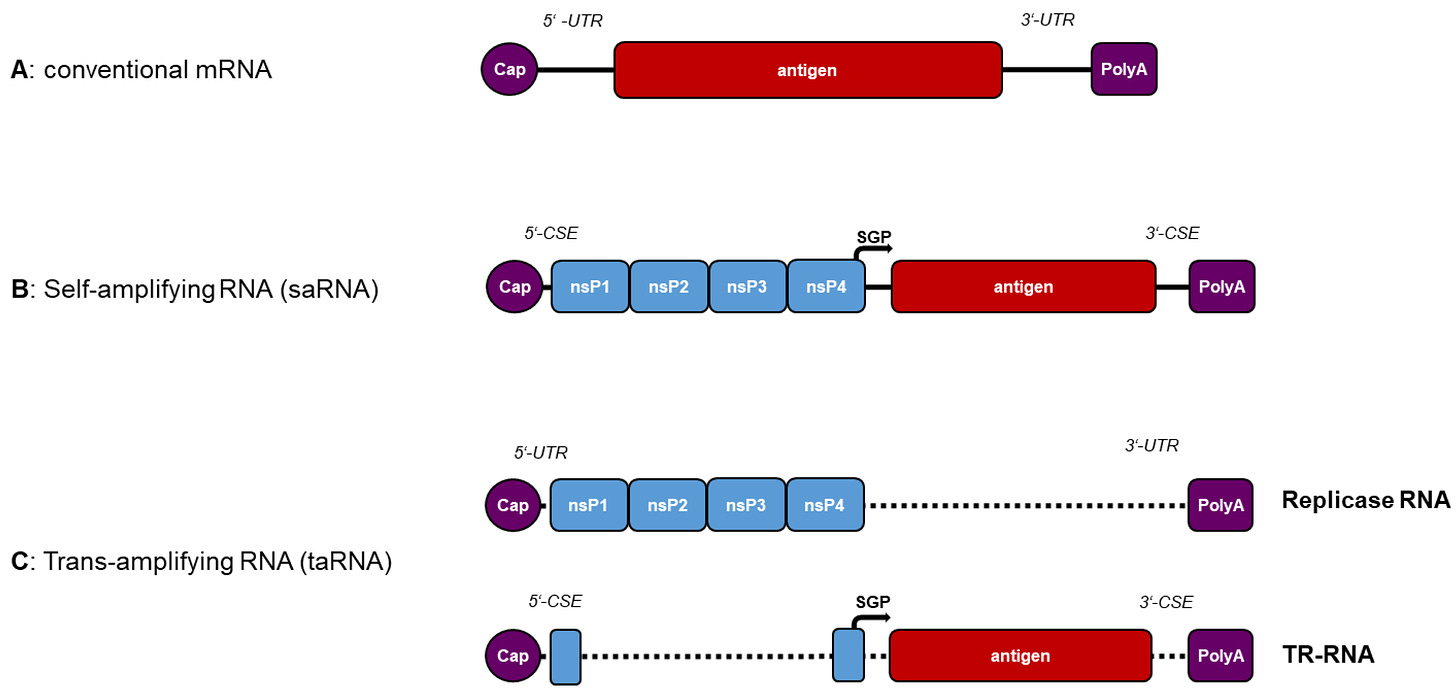
- no indication of how much “amplified mRNA” you’re producing
- no indication of how much spike protein you’re producing
- The viral replicase first uses the positive sense genome as template to synthesize complementary negative sense RNA which subsequently serves as template for the synthesis of genomic and subgenomic plus-strand RNA.
- The subgenomic RNA is produced in excess of the viral genome [24].
- This process leads to high and sustained levels of antigen expression relative to conventional mRNA.
- RNA self-amplification in transfected cells also leads to cellular exhaustion, immune stimulation through dsRNA intermediates and a host cell antiviral response leading to apoptosis.
- In many ways, this process mimics a viral infection and leads to enhance antigen-specific B and T cell responses [75,88]
- “it remains necessary to elucidate how long RNA amplification and antigen expression continues [70].
- After administration of a luciferase saRNA, expression returned to baseline levels after one month [113].
- Moreover, in theory, if the saRNA expresses budding-competent viral glycoproteins, it might be released in vesicles, leading to transfer of the saRNA to additional cells [114]. This should be taken into consideration for the safety evaluation of saRNA vaccines.
- DNA Contamination? Yes please
- “saRNAs and taRNAs are produced like mRNAs from a DNA template by in vitro transcription and the addition of a cap structure.”
- “several approaches to circumvent innate immune activation can be applied; however, for sa/taRNA vaccines, nucleoside modifications will be lost during the amplification step and will be of less benefit”
- In contrast to mRNA vaccines, the intracellular RNA amplification results in dsRNA and thus a stronger activation of innate immune responses. RNA can be recognized by multiple pattern-recognition receptors including TLR3, TLR7, etc.
- The resulting signaling cascades lead to the production of type I interferons (IFN) and pro-inflammatory cytokines [24].
- Although the innate response has an adjuvant effect which can promote the specific immune response, it can also induce RNA degradation and thereby reduce antigen expression [132].
- Strategies to reduce the IFN activation have been described for saRNA vaccines
- LNP formulation also has adjuvant effects
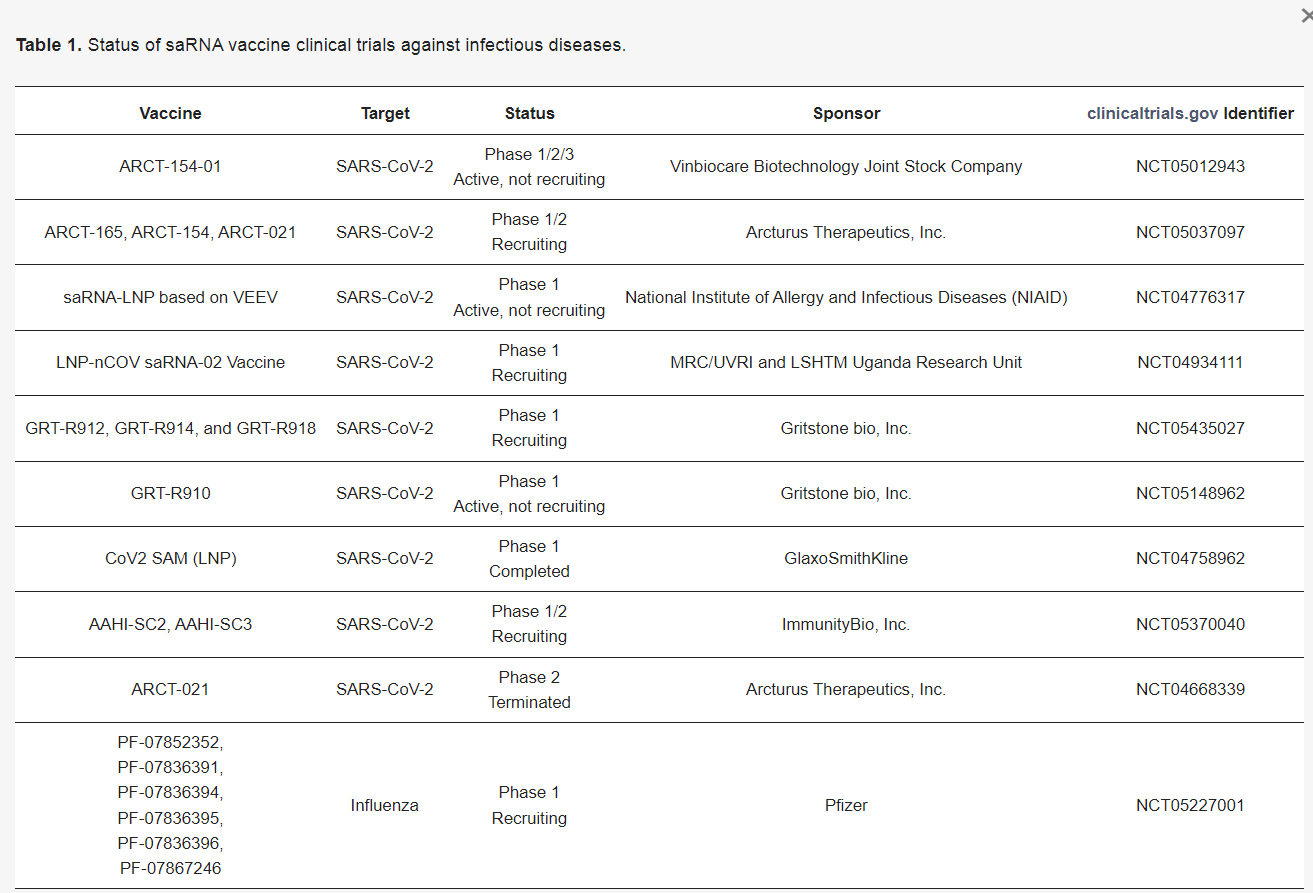
Companies with sa-mRNA in Pipeline:
My Concern…Shedding of Self-Amplifying mRNA
- Pfizer has admitted that its product sheds resulting in “environmental exposure” through inhalation or skin contact.

- But if you’re exposed to a small quantity of Pfizer or Moderna COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine, via LNP/mRNA or exosome/mRNA, it will not vaccinate you.
- Your immune system destroys it.
- But what if you’re exposed to shedding of a SELF-AMPLIFYING mRNA?
- Then theoretically, that mRNA could make unknown quantity of copies of itself in your body for an entire month, and that might be just long enough to cause permanent internal damage.
- This risk has not been studied.

Summary
Japan has approved the world’s first COVID-19 self-amplifying sa-mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine.
Here are some of the problems with this technology:
*
Note to readers: Please click the share button above. Follow us on Instagram and Twitter and subscribe to our Telegram Channel. Feel free to repost and share widely Global Research articles.
Dr. William Makis is a Canadian physician with expertise in Radiology, Oncology and Immunology. Governor General’s Medal, University of Toronto Scholar. Author of 100+ peer-reviewed medical publications.
Featured image is from COVID Intel

