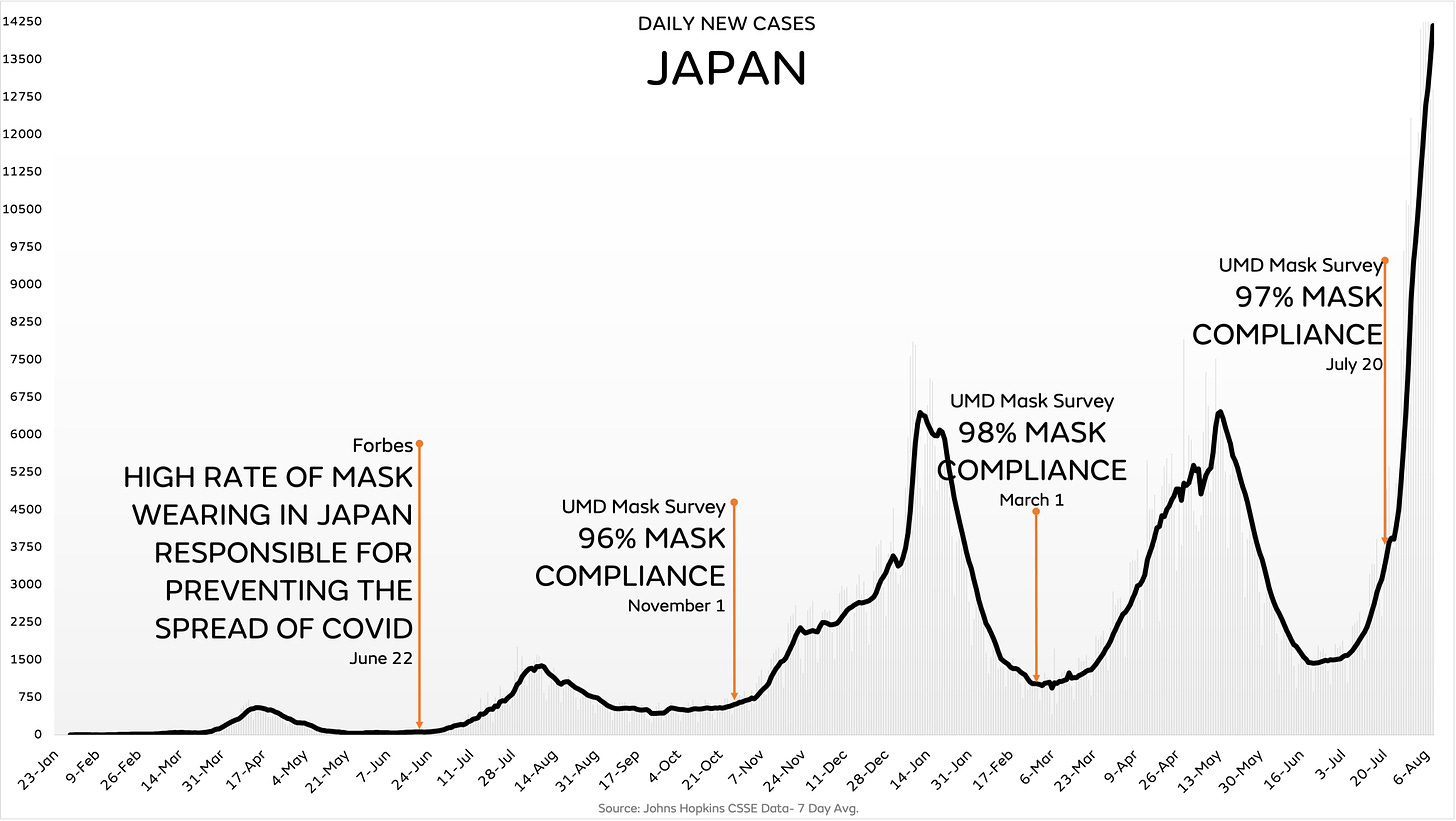
The article below was first published in 2005. Below is a detailed update followed by the original 2005 article.
Author’s Note and Update
The US opioid crisis broadly defined bears a relationship to the export of heroin out of Afghanistan.
How will this multibillion trade (which until recently was protected by US forces) be affected by the withdrawal of US troops from Afghanistan. Private mercenary companies are also involved in supporting the opium trade.
The US withdrawal has been the object of extensive negotiations between US-NATO and the Taliban. A deal was signed in Doha in late February 2020.
Did the U.S. reach a “secret agreement” with the Taliban regarding the opium trade?
Restoration of the Drug Trade. Did the Invasion of Afghanistan Contribute to the Increase in Heroin Addiction
What is important to understand is that one of the key strategic objectives of the 2001 war on Afghanistan was to restore the opium trade following the Taliban government’s successful 2000-2001 drug eradication program which led to a 94% collapse in opium production. This program was supported by the United Nations. (For details, see below)
In the course of the last 19 years following the US-NATO October 2001 invasion, there has been a surge in Afghan opium production. In turn the number of heroin addicts in the US has increased dramatically. Is there a relationship?
There were 189,000 heroin users in the US in 2001, before the US-NATO invasion of Afghanistan.
By 2016 that number went up to 4,500,000 (2.5 million heroin addicts and 2 million casual users).
In 2020, at the hight of the covid crisis, deaths from opioids and drug addiction increased threefold.
It’s Big Money for Big Pharma.
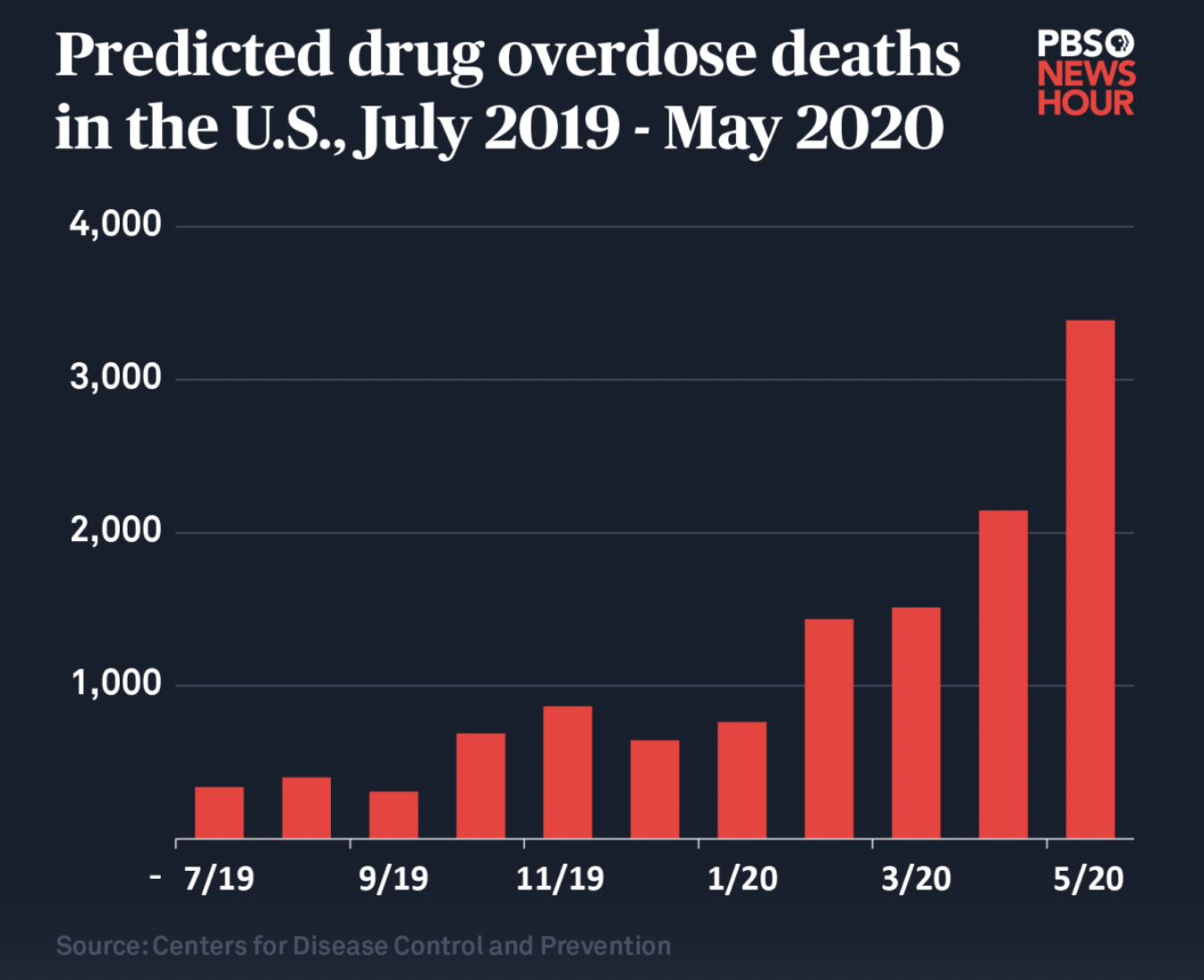
Graph based on CDC data Source PBS
In a bitter irony, Johnson and Johnson which is marketing its “experimental” COVID-19 adenovirus viral vector vaccine, just so happens to be a major producer of prescription opioids.
In November 2020 a “a tentative $26 billion settlement was reached with counties and cities across America which sued J and J and its distributors on behalf of opioid victims.
This class action law suit was “the largest federal court case in American history”. It coincided with the launching of the Covid vaccine initiative in early November 2020. (For further details see Michel Chossudovsky’s E-Book, Chapter VI).

According to the Washington Post:
Johnson & Johnson and the “Big Three” distributors, McKesson, Cardinal Health and Amerisource Bergen, potentially brings a large measure of legal closure for the companies and will funnel money to communities devastated by an addiction crisis that claims more than 70,000 lives in America every year. (emphasis added)
Afghanistan currently produces 84 percent of the World’s opium which feeds the heroin and opioid markets.
Lest we forget, the surge in opium production occurred in the immediate wake of the US invasion in October 2001.
Who is protecting opium exports out of Afghanistan?
“In 2000-2001, the Taliban government –in collaboration with the United Nations– had imposed a successful ban on poppy cultivation. Opium production declined by more than 90 per cent in 2001. In fact the surge in opium cultivation production coincided with the onslaught of the US-led military operation and the downfall of the Taliban regime. From October through December 2001, farmers started to replant poppy on an extensive basis.” (quoted from article below)
The Vienna based UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) reveals that poppy cultivation in 2012 extended over an area of more than 154,000 hectares, an increase of 18% over 2011. A UNODC spokesperson confirmed in 2013 that opium production is heading towards record levels.
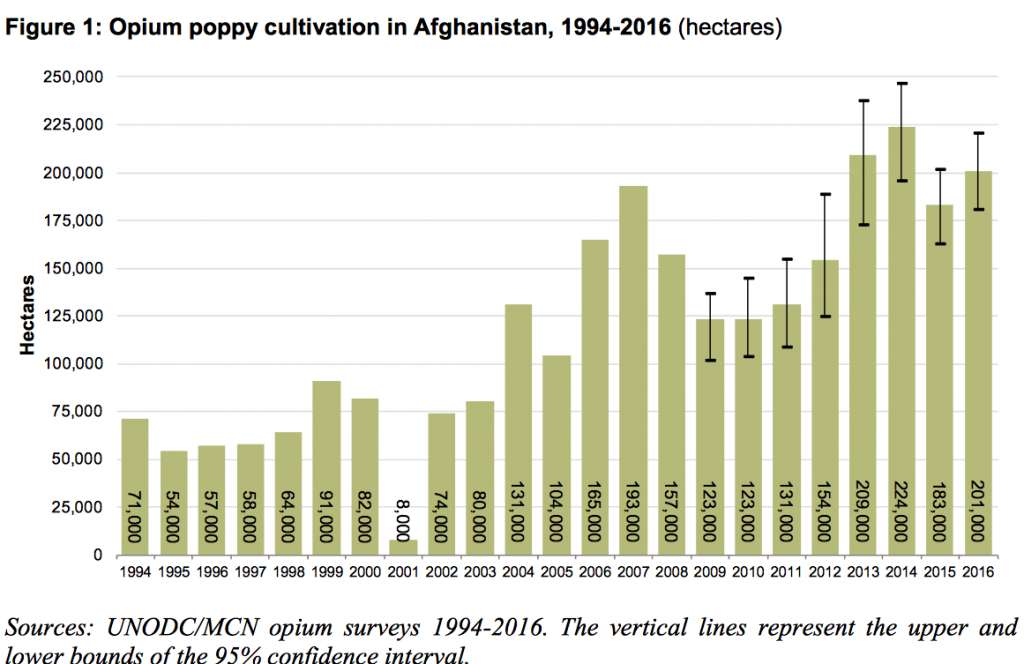
In 2014 the Afghan opium cultivation hit a record high, according to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime’s 2014 Afghan Opium Survey.( See graph below). A slight decline occurred in 2015-2016.
War is good for business. The Afghan opium economy feeds into a lucrative trade in narcotics and money laundering.
Source: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime’s (UNODC)
According to the 2012 Afghanistan Opium Survey released in November 2012 by the Ministry of Counter Narcotics (MCN) and the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). potential opium production in 2012 was of the order of 3,700 tons, a decline of 18 percent in relation to 2001, according to UNODC data.
There is reason to believe that this figure of 3700 tons is grossly underestimated. Moreover, it contradicts the UNOCD’s own predictions of record harvests over an extended area of cultivation.
While bad weather and damaged crops may have played a role as suggested by the UNODC, based on historical trends, the potential production for an area of cultivation of 154,000 hectares, should be well in excess of 6000 tons. With 80,000 hectares in cultivation in 2003, production was already of the order of 3600 tons.
It is worth noting that UNODC has modified the concepts and figures on opium sales and heroin production, as outlined by the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA).
A change in UN methodology in 2010 resulted in a sharp downward revision of Afghan heroin production estimates for 2004 to 2011. UNODC used to estimate that the entire global opium crop was processed into heroin, and provided global heroin production estimates on that basis. Before 2010, a global conversion rate of about 10 kg of opium to 1 kg of heroin was used to estimate world heroin production (17). For instance, the estimated 4 620 tonnes of opium harvested worldwide in 2005 was thought to make it possible to manufacture 472 tonnes of heroin (UNODC, 2009a). However, UNODC now estimates that a large proportion of the Afghan opium harvest is not processed into heroin or morphine but remains ‘available on the drug market as opium’ (UNODC, 2010a). …EU drug markets report: a strategic analysis, EMCDDA, Lisbon, January 2013 emphasis added
 There is no evidence that a large percentage of opium production is no longer processed into heroin as claimed by the UN. This revised UNODC methodology has served, –through the outright manipulation of statistical concepts– to artificially reduce the size of of the global trade in heroin.
There is no evidence that a large percentage of opium production is no longer processed into heroin as claimed by the UN. This revised UNODC methodology has served, –through the outright manipulation of statistical concepts– to artificially reduce the size of of the global trade in heroin.
According to the UNODC, quoted in the EMCDDA report:
“an estimated 3 400 tonnes of Afghan opium was not transformed into heroin or morphine in 2011. Compared with previous years, this is an exceptionally high proportion of the total crop, representing nearly 60 % of the Afghan opium harvest and close to 50 % of the global harvest in 2011.
What the UNODC, –whose mandate is to support the prevention of organized criminal activity– has done is to obfuscate the size and criminal nature of the Afghan drug trade, intimating –without evidence– that a large part of the opium is no longer channeled towards the illegal heroin market.
In 2012 according to the UNODC, farmgate prices for opium were of the order of 196 per kg.
Each kg. of opium produces 100 grams of pure heroin. The US retail prices for heroin (with a low level of purity) is, according to UNODC of the order of $172 a gram. The price per gram of pure heroin is substantially higher.
The profits are largely reaped at the level of the international wholesale and retail markets of heroin as well as in the process of money laundering in Western banking institutions.
The revenues derived from the global trade in heroin constitute a multibillion dollar bonanza for financial institutions and organized crime.
.
Record Production in 2016. Fake Eradication Program
.
.
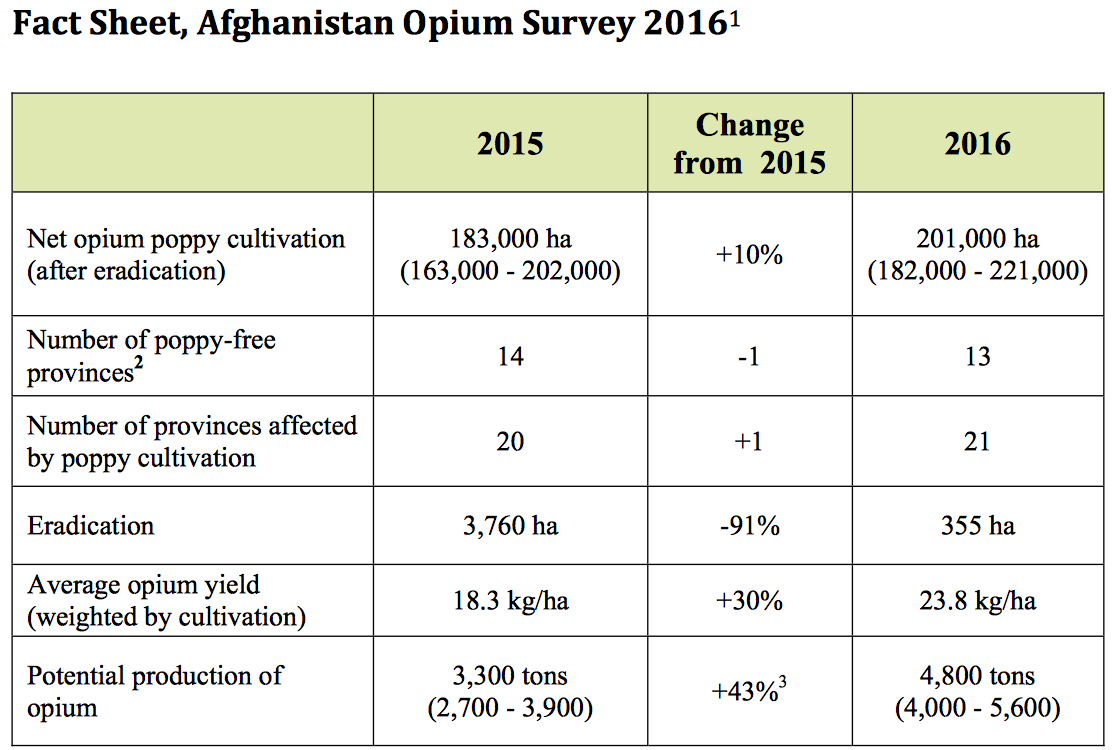
“Opium production in Afghanistan rose by 43 per cent to 4,800 metric tons in 2016 compared with 2015 levels, according to the latest
Afghanistan Opium Survey figures released today by the Afghan Ministry of Counter Narcotics and the UNODC. The area under opium poppy cultivation also increased to 201,000 hectares (ha) in 2016, a rise of 10 per cent compared with 183,000 ha in 2015.
.
This represents a twentyfold increase in the areas under opium cultivation since the US invasion in October 2001. In 2016, opium production had increased by approximately 25 times in relation to its 2001 levels, from 185 tons in 2001 to 4800 tons in 2016.
.
Source: UNODC
The following article first published in May 2005 provides a background on the history of the Afghan opium trade which until recently was protected by US-NATO occupation forces on behalf of powerful financial interests.
Michel Chossudovsky, May 2o16, August 2021
The Spoils of War: Afghanistan’s Multibillion Dollar Heroin Trade
by Michel Chossudovsky
Global Research, May 2005
Since the US led invasion of Afghanistan in October 2001, the Golden Crescent opium trade has soared. According to the US media, this lucrative contraband is protected by Osama, the Taliban, not to mention, of course, the regional warlords, in defiance of the “international community”.
The heroin business is said to be “filling the coffers of the Taliban”. In the words of the US State Department:
“Opium is a source of literally billions of dollars to extremist and criminal groups… [C]utting down the opium supply is central to establishing a secure and stable democracy, as well as winning the global war on terrorism,” (Statement of Assistant Secretary of State Robert Charles. Congressional Hearing, 1 April 2004)
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), opium production in Afghanistan in 2003 is estimated at 3,600 tons, with an estimated area under cultivation of the order of 80,000 hectares. (UNODC at http://www.unodc.org/unodc/index.html ).An even larger bumper harvest is predicted for 2004.
The State Department suggests that up to 120 000 hectares were under cultivation in 2004. (Congressional Hearing, op cit):
“We could be on a path for a significant surge. Some observers indicate perhaps as much as 50 percent to 100 percent growth in the 2004 crop over the already troubling figures from last year.”(Ibid)
“Operation Containment“
In response to the post-Taliban surge in opium production, the Bush administration has boosted its counter terrorism activities, while allocating substantial amounts of public money to the Drug Enforcement Administration’s West Asia initiative, dubbed “Operation Containment.”
The various reports and official statements are, of course, blended in with the usual “balanced” self critique that “the international community is not doing enough”, and that what we need is “transparency”.
The headlines are “Drugs, warlords and insecurity overshadow Afghanistan’s path to democracy”. In chorus, the US media is accusing the defunct “hard-line Islamic regime”, without even acknowledging that the Taliban –in collaboration with the United Nations– had imposed a successful ban on poppy cultivation in 2000. Opium production declined by more than 90 per cent in 2001. In fact the surge in opium cultivation production coincided with the onslaught of the US-led military operation and the downfall of the Taliban regime. From October through December 2001, farmers started to replant poppy on an extensive basis.
The success of Afghanistan’s 2000 drug eradication program under the Taliban had been acknowledged at the October 2001 session of the UN General Assembly (which took place barely a few days after the beginning of the 2001 bombing raids). No other UNODC member country was able to implement a comparable program:
“Turning first to drug control, I had expected to concentrate my remarks on the implications of the Taliban’s ban on opium poppy cultivation in areas under their control… We now have the results of our annual ground survey of poppy cultivation in Afghanistan. This year’s production [2001] is around 185 tons. This is down from the 3300 tons last year [2000], a decrease of over 94 per cent. Compared to the record harvest of 4700 tons two years ago, the decrease is well over 97 per cent.
Any decrease in illicit cultivation is welcomed, especially in cases like this when no displacement, locally or in other countries, took place to weaken the achievement”
(Remarks on behalf of UNODC Executive Director at the UN General Assembly, Oct 2001, http://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/speech_2001-10-12_1.html )
United Nations’ Coverup
In the wake of the US invasion, shift in rhetoric. UNODC is now acting as if the 2000 opium ban had never happened:
“the battle against narcotics cultivation has been fought and won in other countries and it [is] possible to do so here [in Afghanistan], with strong, democratic governance, international assistance and improved security and integrity.”
( Statement of the UNODC Representative in Afghanistan at the :February 2004 International Counter Narcotics Conference, p. 5).
In fact, both Washington and the UNODC now claim that the objective of the Taliban in 2000 was not really “drug eradication” but a devious scheme to trigger “an artificial shortfall in supply”, which would drive up World prices of heroin.
Ironically, this twisted logic, which now forms part of a new “UN consensus”, is refuted by a report of the UNODC office in Pakistan, which confirmed, at the time, that there was no evidence of stockpiling by the Taliban. (Deseret News, Salt Lake City, Utah. 5 October 2003)
Washington’s Hidden Agenda: Restore the Drug Trade
In the wake of the 2001 US bombing of Afghanistan, the British government of Tony Blair was entrusted by the G-8 Group of leading industrial nations to carry out a drug eradication program, which would, in theory, allow Afghan farmers to switch out of poppy cultivation into alternative crops. The British were working out of Kabul in close liaison with the US DEA’s “Operation Containment”.
The UK sponsored crop eradication program is an obvious smokescreen. Since October 2001, opium poppy cultivation has skyrocketed. The presence of occupation forces in Afghanistan did not result in the eradication of poppy cultivation. Quite the opposite.
The Taliban prohibition had indeed caused “the beginning of a heroin shortage in Europe by the end of 2001”, as acknowledged by the UNODC.
Heroin is a multibillion dollar business supported by powerful interests, which requires a steady and secure commodity flow. One of the “hidden” objectives of the war was precisely to restore the CIA sponsored drug trade to its historical levels and exert direct control over the drug routes.
Immediately following the October 2001 invasion, opium markets were restored. Opium prices spiraled. By early 2002, the opium price (in dollars/kg) was almost 10 times higher than in 2000.
In 2001, under the Taliban opiate production stood at 185 tons, increasing to 3400 tons in 2002 under the US sponsored puppet regime of President Hamid Karzai.
While highlighting Karzai’s patriotic struggle against the Taliban, the media fails to mention that Karzai collaborated with the Taliban. He had also been on the payroll of a major US oil company, UNOCAL. In fact, since the mid-1990s, Hamid Karzai had acted as a consultant and lobbyist for UNOCAL in negotiations with the Taliban. According to the Saudi newspaper Al-Watan:
“Karzai has been a Central Intelligence Agency covert operator since the 1980s. He collaborated with the CIA in funneling U.S. aid to the Taliban as of 1994 when the Americans had secretly and through the Pakistanis [specifically the ISI] supported the Taliban’s assumption of power.” (quoted in Karen Talbot, U.S. Energy Giant Unocal Appoints Interim Government in Kabul, Global Outlook, No. 1, Spring 2002. p. 70. See also BBC Monitoring Service, 15 December 2001)
History of the Golden Crescent Drug trade
It is worth recalling the history of the Golden Crescent drug trade, which is intimately related to the CIA’s covert operations in the region since the onslaught of the Soviet-Afghan war and its aftermath.
Prior to the Soviet-Afghan war (1979-1989), opium production in Afghanistan and Pakistan was directed to small regional markets. There was no local production of heroin. (Alfred McCoy, Drug Fallout: the CIA’s Forty Year Complicity in the Narcotics Trade. The Progressive, 1 August 1997).
The Afghan narcotics economy was a carefully designed project of the CIA, supported by US foreign policy.
As revealed in the Iran-Contra and Bank of Commerce and Credit International (BCCI) scandals, CIA covert operations in support of the Afghan Mujahideen had been funded through the laundering of drug money. “Dirty money” was recycled –through a number of banking institutions (in the Middle East) as well as through anonymous CIA shell companies–, into “covert money,” used to finance various insurgent groups during the Soviet-Afghan war, and its aftermath:
“Because the US wanted to supply the Mujahideen rebels in Afghanistan with stinger missiles and other military hardware it needed the full cooperation of Pakistan. By the mid-1980s, the CIA operation in Islamabad was one of the largest US intelligence stations in the World. `If BCCI is such an embarrassment to the US that forthright investigations are not being pursued it has a lot to do with the blind eye the US turned to the heroin trafficking in Pakistan’, said a US intelligence officer. (“The Dirtiest Bank of All,” Time, July 29, 1991, p. 22.)
Researcher Alfred McCoy’s study confirms that within two years of the onslaught of the CIA’s covert operation in Afghanistan in 1979,
“the Pakistan-Afghanistan borderlands became the world’s top heroin producer, supplying 60 per cent of U.S. demand. In Pakistan, the heroin-addict population went from near zero in 1979 to 1.2 million by 1985, a much steeper rise than in any other nation.”
“CIA assets again controlled this heroin trade. As the Mujahideen guerrillas seized territory inside Afghanistan, they ordered peasants to plant opium as a revolutionary tax. Across the border in Pakistan, Afghan leaders and local syndicates under the protection of Pakistan Intelligence operated hundreds of heroin laboratories. During this decade of wide-open drug-dealing, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency in Islamabad failed to instigate major seizures or arrests.
U.S. officials had refused to investigate charges of heroin dealing by its Afghan allies because U.S. narcotics policy in Afghanistan has been subordinated to the war against Soviet influence there. In 1995, the former CIA director of the Afghan operation, Charles Cogan, admitted the CIA had indeed sacrificed the drug war to fight the Cold War. ‘Our main mission was to do as much damage as possible to the Soviets. We didn’t really have the resources or the time to devote to an investigation of the drug trade,’ I don’t think that we need to apologize for this. Every situation has its fallout. There was fallout in terms of drugs, yes. But the main objective was accomplished. The Soviets left Afghanistan.'”(McCoy, op cit)
The role of the CIA, which is amply documented, is not mentioned in official UNODC publications, which focus on internal social and political factors. Needless to say, the historical roots of the opium trade have been grossly distorted.
(See UNODC http://www.unodc.org/pdf/publications/afg_opium_economy_www.pdf
According to the UNODC, Afghanistan’s opium production has increased, more than 15-fold since 1979. In the wake of the Soviet-Afghan war, the growth of the narcotics economy has continued unabated. The Taliban, which were supported by the US, were initially instrumental in the further growth of opiate production until the 2000 opium ban.
(See UNODC http://www.unodc.org/pdf/publications/afg_opium_economy_www.pdf
This recycling of drug money was used to finance the post-Cold War insurgencies in Central Asia and the Balkans including Al Qaeda. (For details, see Michel Chossudovsky, War and Globalization, The Truth behind September 11, Global Outlook, 2002, http://globalresearch.ca/globaloutlook/truth911.html )
Narcotics: Second to Oil and the Arms Trade
The revenues generated from the CIA sponsored Afghan drug trade are sizeable. The Afghan trade in opiates constitutes a large share of the worldwide annual turnover of narcotics, which was estimated by the United Nations to be of the order of $400-500 billion. (Douglas Keh, Drug Money in a Changing World, Technical document No. 4, 1998, Vienna UNDCP, p. 4. See also United Nations Drug Control Program, Report of the International Narcotics Control Board for 1999, E/INCB/1999/1 United Nations, Vienna 1999, p. 49-51, and Richard Lapper, UN Fears Growth of Heroin Trade, Financial Times, 24 February 2000). At the time these UN figures were first brought out (1994), the (estimated) global trade in drugs was of the same order of magnitude as the global trade in oil.
The IMF estimated global money laundering to be between 590 billion and 1.5 trillion dollars a year, representing 2-5 percent of global GDP. (Asian Banker, 15 August 2003). A large share of global money laundering as estimated by the IMF is linked to the trade in narcotics.
Based on recent figures (2003), drug trafficking constitutes “the third biggest global commodity in cash terms after oil and the arms trade.” (The Independent, 29 February 2004).
Moreover, the above figures including those on money laundering, confirm that the bulk of the revenues associated with the global trade in narcotics are not appropriated by terrorist groups and warlords, as suggested by the UNODC report.
There are powerful business and financial interests behind narcotics. From this standpoint, geopolitical and military control over the drug routes is as strategic as oil and oil pipelines.
However, what distinguishes narcotics from legal commodity trade is that narcotics constitutes a major source of wealth formation not only for organised crime but also for the US intelligence apparatus, which increasingly constitutes a powerful actor in the spheres of finance and banking.
In turn, the CIA, which protects the drug trade, has developed complex business and undercover links to major criminal syndicates involved in the drug trade.
In other words, intelligence agencies and powerful business syndicates allied with organized crime, are competing for the strategic control over the heroin routes. The multi-billion dollar revenues of narcotics are deposited in the Western banking system. Most of the large international banks together with their affiliates in the offshore banking havens launder large amounts of narco-dollars.
This trade can only prosper if the main actors involved in narcotics have “political friends in high places.” Legal and illegal undertakings are increasingly intertwined, the dividing line between “businesspeople” and criminals is blurred. In turn, the relationship among criminals, politicians and members of the intelligence establishment has tainted the structures of the state and the role of its institutions.
Where does the money go? Who benefits from the Afghan opium trade?
This trade is characterized by a complex web of intermediaries. There are various stages of the drug trade, several interlocked markets, from the impoverished poppy farmer in Afghanistan to the wholesale and retail heroin markets in Western countries. In other words, there is a “hierarchy of prices” for opiates.
This hierarchy of prices is acknowledged by the US administration:
“Afghan heroin sells on the international narcotics market for 100 times the price farmers get for their opium right out of the field”.(US State Department quoted by the Voice of America (VOA), 27 February 2004).
According to the UNODC, opium in Afghanistan generated in 2003 “an income of one billion US dollars for farmers and US$ 1.3 billion for traffickers, equivalent to over half of its national income.”
Consistent with these UNODC estimates, the average price for fresh opium was $350 a kg. (2002); the 2002 production was 3400 tons. (http://www.poppies.org/news/104267739031389.shtml ).
The UNDOC estimate, based on local farmgate and wholesale prices constitutes, however, a very small percentage of the total turnover of the multibillion dollar Afghan drug trade. The UNODC, estimates “the total annual turn-over of international trade” in Afghan opiates at US$ 30 billion. An examination of the wholesale and retail prices for heroin in the Western countries suggests, however, that the total revenues generated, including those at the retail level, are substantially higher.
Wholesale Prices of Heroin in Western Countries
It is estimated that one kilo of opium produces approximately 100 grams of (pure) heroin. The US DEA confirms that “SWA [South West Asia meaning Afghanistan] heroin in New York City was selling in the late 1990s for $85,000 to $190,000 per kilogram wholesale with a 75 percent purity ratio (National Drug Intelligence Center, http://www.usdoj.gov/ndic/pubs/648/ny_econ.htm ).
According to the US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) “the price of SEA [South East Asian] heroin ranges from $70,000 to $100,000 per unit (700 grams) and the purity of SEA heroin ranges from 85 to 90 percent” (ibid). The SEA unit of 700 gr (85-90 % purity) translates into a wholesale price per kg. for pure heroin ranging between $115,000 and $163,000.
The DEA figures quoted above, while reflecting the situation in the 1990s, are broadly consistent with recent British figures. According to a report published in the Guardian (11 August 2002), the wholesale price of (pure) heroin in London (UK) was of the order of 50,000 pounds sterling, approximately $80,000 (2002).
Whereas as there is competition between different sources of heroin supply, it should be emphasized that Afghan heroin represents a rather small percentage of the US heroin market, which is largely supplied out of Colombia.
Retail Prices
US
“The NYPD notes that retail heroin prices are down and purity is relatively high. Heroin previously sold for about $90 per gram but now sells for $65 to $70 per gram or less. Anecdotal information from the NYPD indicates that purity for a bag of heroin commonly ranges from 50 to 80 percent but can be as low as 30 percent. Information as of June 2000 indicates that bundles (10 bags) purchased by Dominican buyers from Dominican sellers in larger quantities (about 150 bundles) sold for as little as $40 each, or $55 each in Central Park. DEA reports that an ounce of heroin usually sells for $2,500 to $5,000, a gram for $70 to $95, a bundle for $80 to $90, and a bag for $10. The DMP reports that the average heroin purity at the street level in 1999 was about 62 percent.” (National Drug Intelligence Center, http://www.usdoj.gov/ndic/pubs/648/ny_econ.htm ).
The NYPD and DEA retail price figures seem consistent. The DEA price of $70-$95, with a purity of 62 percent translates into $112 to $153 per gram of pure heroin. The NYPD figures are roughly similar with perhaps lower estimates for purity.
It should be noted that when heroin is purchased in very small quantities, the retail price tends to be much higher. In the US, purchase is often by “the bag”; the typical bag according to Rocheleau and Boyum contains 25 milligrams of pure heroin.
(http://www.whitehousedrugpolicy.gov/publications/drugfact/american_users_spend/appc.html )
A $10 dollar bag in NYC (according to the DEA figure quoted above) would convert into a price of $400 per gram, each bag containing 0.025gr. of pure heroin. (op cit). In other words, for very small purchases marketed by street pushers, the retail margin tends to be significantly higher. In the case of the $10 bag purchase, it is roughly 3 to 4 times the corresponding retail price per gram.($112-$153)
UK
In Britain, the retail street price per gram of heroin, according to British Police sources, “has fallen from £74 in 1997 to £61 [in 2004].” [i.e. from approximately $133 to $110, based on the 2004 rate of exchange] (Independent, 3 March 2004). In some cities it was as low as £30-40 per gram with a low level of purity. (AAP News, 3 March 2004). According to Drugscope (http://www.drugscope.org.uk/ ), the average price for a gram of heroin in Britain is between £40 and £90 ($72- $162 per gram) (The report does not mention purity). The street price of heroin was £60 per gram in April 2002 according to the National Criminal Intelligence Service.
(See:http://www.drugscope.org.uk/druginfo/drugsearch/ds_results.asp?file=%5Cwip%5C11%5C1%5C1%5Cheroin_opiates.html )
The Hierarchy of Prices
We are dealing with a hierarchy of prices, from the farmgate price in the producing country, upwards, to the final retail street price. The latter is often 80-100 times the price paid to the farmer.
In other words, the opiate product transits through several markets from the producing country to the transshipment country(ies), to the consuming countries. In the latter, there are wide margins between “the landing price” at the point of entry, demanded by the drug cartels and the wholesale prices and the retail street prices, protected by Western organized crime.
The Global Proceeds of the Afghan Narcotics Trade
In Afghanistan, the reported production of 3600 tons of opium in 2003 would allow for the production of approximately 360,000 kg of pure heroin. Gross revenues accruing to Afghan farmers are roughly estimated by the UNODC to be of the order of $1 billion, with 1.3 billion accruing to local traffickers.
When sold in Western markets at a heroin wholesale price of the order of $100,000 a kg (with a 70 percent purity ratio), the global wholesale proceeds (corresponding to 3600 tons of Afghan opium) would be of the order of 51.4 billion dollars. The latter constitutes a conservative estimate based on the various figures for wholesale prices in the previous section.
The total proceeds of the Afghan narcotics trade (in terms of total value added) is estimated using the final heroin retail price. In other words, the retail value of the trade is ultimately the criterion for measuring the importance of the drug trade in terms of revenue generation and wealth formation.
A meaningful estimate of the retail value, however, is almost impossible to ascertain due to the fact that retail prices vary considerably within urban areas, from one city to another and between consuming countries, not to mention variations in purity and quality (see above).
The evidence on retail margins, namely the difference between wholesale and retail values in the consuming countries, nonetheless, suggests that a large share of the total (money) proceeds of the drug trade are generated at the retail level.
In other words, a significant portion of the proceeds of the drug trade accrues to criminal and business syndicates in Western countries involved in the local wholesale and retail narcotics markets. And the various criminal gangs involved in retail trade are invariably protected by the “corporate” crime syndicates.
90 percent of heroin consumed in the UK is from Afghanistan. Using the British retail price figure from UK police sources of $110 a gram (with an assumed 50 percent purity level), the total retail value of the Afghan narcotics trade in 2003 (3600 tons of opium) would be the order of 79.2 billion dollars. The latter should be considered as a simulation rather than an estimate.
Under this assumption (simulation), a billion dollars gross revenue to the farmers in Afghanistan (2003) would generate global narcotics earnings, –accruing at various stages and in various markets– of the order of 79.2 billion dollars. These global proceeds accrue to business syndicates, intelligence agencies, organized crime, financial institutions, wholesalers, retailers, etc. involved directly or indirectly in the drug trade.
In turn, the proceeds of this lucrative trade are deposited in Western banks, which constitute an essential mechanism in the laundering of dirty money.
A very small percentage accrues to farmers and traders in the producing country. Bear in mind that the net income accruing to Afghan farmers is but a fraction of the estimated 1 billion dollar amount. The latter does not include payments of farm inputs, interest on loans to money lenders, political protection, etc.
(See also UNODC, The Opium Economy in Afghanistan, http://www.unodc.org/pdf/publications/afg_opium_economy_www.pdf , Vienna, 2003, p. 7-8)
The Share of the Afghan Heroin in the Global Drug Market
Afghanistan produces over 70 percent of the global supply of heroin and heroin represents a sizeable fraction of the global narcotics market, estimated by the UN to be of the order of $400-500 billion.
There are no reliable estimates on the distribution of the global narcotics trade between the main categories: Cocaine, Opium/Heroin, Cannabis, Amphetamine Type Stimulants (ATS), Other Drugs.
The Laundering of Drug Money
The proceeds of the drug trade are deposited in the banking system. Drug money is laundered in the numerous offshore banking havens in Switzerland, Luxembourg, the British Channel Islands, the Cayman Islands and some 50 other locations around the globe. It is here that the criminal syndicates involved in the drug trade and the representatives of the world’s largest commercial banks interact. Dirty money is deposited in these offshore havens, which are controlled by the major Western commercial banks. The latter have a vested interest in maintaining and sustaining the drug trade. (For further details, see Michel Chossudovsky, The Crimes of Business and the Business of Crimes, Covert Action Quarterly, Fall 1996)
Once the money has been laundered, it can be recycled into bona fide investments not only in real estate, hotels, etc, but also in other areas such as the services economy and manufacturing. Dirty and covert money is also funneled into various financial instruments including the trade in derivatives, primary commodities, stocks, and government bonds.
Concluding Remarks: Criminalization of US Foreign Policy
US foreign policy supports the workings of a thriving criminal economy in which the demarcation between organized capital and organized crime has become increasingly blurred.
The heroin business is not “filling the coffers of the Taliban” as claimed by US government and the international community: quite the opposite! The proceeds of this illegal trade are the source of wealth formation, largely reaped by powerful business/criminal interests within the Western countries. These interests are sustained by US foreign policy.
Decision-making in the US State Department, the CIA and the Pentagon is instrumental in supporting this highly profitable multibillion dollar trade, third in commodity value after oil and the arms trade.
The Afghan drug economy is “protected”.
The heroin trade was part of the war agenda. What this war has achieved is to restore a compliant narco-State, headed by a US appointed puppet.
The powerful financial interests behind narcotics are supported by the militarisation of the world’s major drug triangles (and transshipment routes), including the Golden Crescent and the Andean region of South America (under the so-called Andean Initiative).
Table 1
Opium Poppy Cultivation in Afghanistan
Year Cultivation in hectares Production (tons)
1994 71,470 3,400
1995 53,759 2,300
1996 56,824 2,200
1997 58,416 2,800
1998 63,674 2,700
1999 90,983 4,600
2000 82,172 3,300
2001 7,606 185
2002 74 000 3400
2003 80 000 3600
Source: UNDCP, Afghanistan, Opium Poppy Survey, 2001, UNOCD, Opium Poppy Survey, 2002. http://www.unodc.org/pdf/afg/afg_opium_survey_2002.pdf
See also Press Release: http://www.unodc.org/unodc/press_release_2004-03-31_1.html , and 2003 Survey: http://www.unodc.org/pdf/afg/afghanistan_opium_survey_2003.pdf
Notice the dip in 2001













 Edward Curtin is the author of Seeking the Truth in a Country of Lies
Edward Curtin is the author of Seeking the Truth in a Country of Lies