Mosquitoes Harnessed to Vaccinate Humans Without Consent
New England Journal of Medicine Report of Malaria Vaccine Delivered by Mosquito Bites

It seems as if the world of vaccinology has ramped up to a feverish pitch with amplified research, massive funding, and no limit to the extent in which vaccines could be injected into humans. Dr. McCullough was a December 31, 2024, guest on the Grant Stinchfield Podcast to review research using mosquitoes to deliver vaccines to humans through their nasty bites in the skin.
Lamers et al described experiments where mosquitoes were laced with a malaria vaccine and then normal human volunteers went through three session of 50 bites each to get “vaccinated.” It took only five bites to give the subjects a case of controlled malaria infection.
Stinchfield raised the ethical considerations of this line of development where mosquitoes released into nature essentially like flying syringes could vaccinate people without informed consent, no control over dose, prior immunity, and no ability to recognize or report side effects. Please enjoy this interview which also includes a review and clips from mosquito labs around the world demonstrating the massive resources poured into this line of development unfortunately with very poor biosecurity in some parts of the world.
Below is an excerpt from the NEJM article.
***
Safety and Efficacy of Immunization with a Late-Liver-Stage Attenuated Malaria Parasite
Authors: Olivia A.C. Lamers, M.D., Blandine M.D. Franke-Fayard, Ph.D., Jan Pieter R. Koopman, M.D., Geert V.T. Roozen, M.D., Jacqueline J. Janse, M.Sc., Severine C. Chevalley-Maurel, M.Sc., Fiona J.A. Geurten, B.Sc., Helena M. de Bes-Roeleveld, B.Sc., Eva Iliopoulou, M.Sc., Emil Colstrup, M.Sc. Els Wessels, Ph.D., Geert-Jan van Gemert, B.Sc., Margavan de Vegte-Bolmer, B.Sc., Wouter Graumans, Ph.D., Thabitha R. Stoter, B.Sc., Benjamin G. Mordmüller, M.D., Emma L.Houlder, Ph.D., Teun Bousema, Ph.D., Rajagopal Murugan, Ph.D., Matthew B.B. McCall, M.D., Ph.D., Chris J. Janse, Ph.D., and Meta Roestenberg, M.D., Ph.D.
Published November 20, 2024, N Engl J Med 2024;391:1913-1923, DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2313892
.
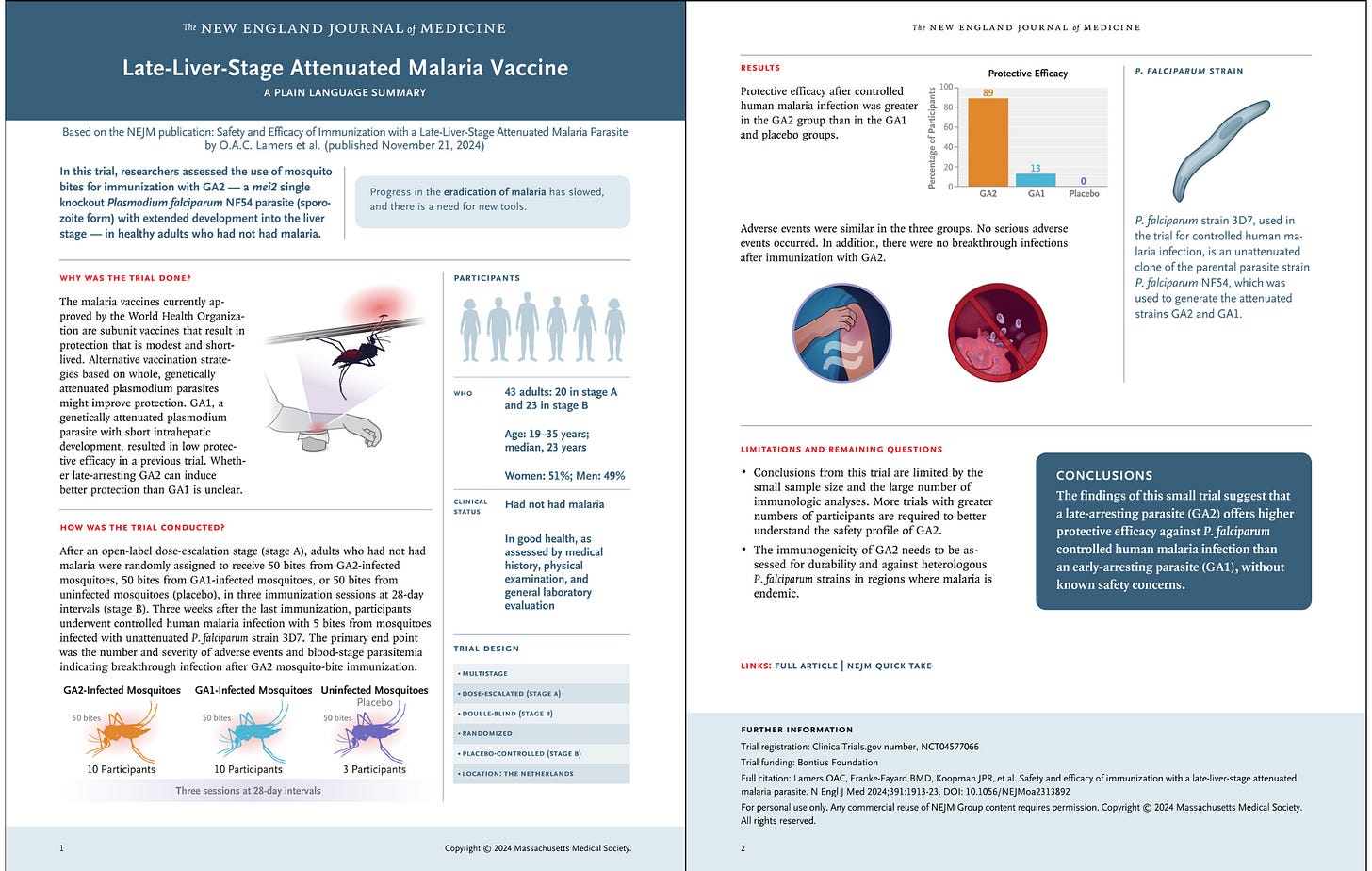
Download a PDF of the Plain Language Summary.
.
Abstract
Background
Currently licensed and approved malaria subunit vaccines provide modest, short-lived protection against malaria. Immunization with live-attenuated Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites is an alternative vaccination strategy that has potential to improve protection.
Methods
We conducted a double-blind, controlled clinical trial to evaluate the safety, side-effect profile, and efficacy of immunization, by means of mosquito bites, with a second-generation genetically attenuated parasite (GA2) — a mei2 single knockout P. falciparum NF54 parasite (sporozoite form) with extended development into the liver stage. After an open-label dose-escalation safety phase in which participants were exposed to the bites of 15 or 50 infected mosquitoes (stage A), healthy adults who had not had malaria were randomly assigned to be exposed to 50 mosquito bites per immunization of GA2, an early-arresting parasite (GA1), or placebo (bites from uninfected mosquitoes) (stage B). After the completion of three immunization sessions with 50 mosquito bites per session, we compared the protective efficacy of GA2 against homologous P. falciparum controlled human malaria infection with that of GA1 and placebo. The primary end points were the number and severity of adverse events (in stages A and B) and blood-stage parasitemia greater than 100 P. falciparum parasites per milliliter after bites from GA2-infected mosquitoes (in stage A) and after controlled human malaria infection (in stage B).
Results
Adverse events were similar across the trial groups. Protective efficacy against subsequent controlled human malaria infection was observed in 8 of 9 participants (89%) in the GA2 group, in 1 of 8 participants (13%) in the GA1 group, and in 0 of 3 participants in the placebo group. A significantly higher frequency of P. falciparum–specific polyfunctional CD4+ and Vδ2+ γδ T cells were observed among participants who received GA2 than among those who received GA1, whereas GA2 and GA1 induced similar antibody titers targeting the P. falciparum circumsporozoite protein.
Conclusions
In this small trial, GA2 was associated with a favorable immune induction profile and protective efficacy, findings that warrant further evaluation. (Funded by the Bontius Foundation; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04577066.)
*
Click the share button below to email/forward this article. Follow us on Instagram and X and subscribe to our Telegram Channel. Feel free to repost Global Research articles with proper attribution.
Global Research is a reader-funded media. We do not accept any funding from corporations or governments. Help us stay afloat. Click the image below to make a one-time or recurring donation.


