Birds, Other Wildlife Sacrificed for Useless Mask Pollution
All Global Research articles can be read in 51 languages by activating the “Translate Website” drop down menu on the top banner of our home page (Desktop version).
To receive Global Research’s Daily Newsletter (selected articles), click here.
Follow us on Instagram and Twitter and subscribe to our Telegram Channel. Feel free to repost and share widely Global Research articles.
***
Worldwide reports, including from Sri Lanka, the U.K, Australia, Japan and North America were gathered to demonstrate how masks have created environmental pollution that is injuring and killing wildlife
Mindless mask mandates increase your risk of death, weaken the immune system, encourage dehydration, increase headaches, decrease cognitive precision and promote facial alkalinization
Wearing surgical masks increases your daily inhalation of microplastics, while studies have demonstrated that mask wearing does not lower your risk of contracting viral illnesses, including flu and COVID-19
*
Yet another way in which masks have created problems is the environmental pollution that is injuring and killing wildlife.1,2,3 Experts have estimated that 129 billion face masks and 65 billion gloves were used and discarded each month during the pandemic. In 2020, research also suggested that 1.6 billion disposable masks from mindless mask mandates ended up in the ocean.4
But it’s not just the whole masks and gloves that have created a significant environmental problem. Although the bottled water crisis is a leading source of environmental plastic pollution, the new mask crisis is slated to outpace it. The scientists in one paper5 published in Frontiers of Environmental Science and Engineering wrote:
“… there is no official guidance on mask recycling, making it more likely to be disposed of as solid waste. With increasing reports on inappropriate disposal of masks, it is urgent to recognize this potential environmental threat.”
Masks are not being recycled. Yet, their material makes it likely they persist and accumulate in the environment. Most disposable surgical masks contain three layers — polyester outer layer, a polypropylene or polystyrene middle layer and an inner layer made of absorbent materials such as cotton.
Polypropylene is one of the most problematic plastics, as it’s widely produced, responsible for a large accumulation of waste in the environment, and is a known asthma trigger.6 The researchers noted7 that once masks are subjected to solar radiation, the degradation of polypropylene slows dramatically and leads to persistence and accumulation.
But, before the masks even break down in the environment, they are causing significant damage to wildlife, especially the bird population. You don’t have to be a bird enthusiast to understand that birds are uniquely important to the balance of the environment.
They are pollinators, they disperse seeds and they recycle nutrients.8 They are predators, scavengers and ecosystem engineers. Injuries and falling populations will have a unique and significant impact on an ecosystem on which we rely for our survival.
COVID Face Masks Devastating Wildlife
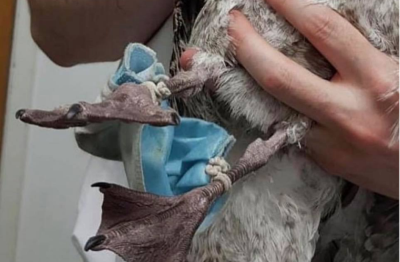
Researchers used social media images to identify the effect personal protective equipment waste has had on wildlife, including disposable masks and gloves. Information from the online citizen science project, Birds and Debris,9 and Dalhousie University reveal the devastation to wildlife, especially birds.
Birds and Debris has been collecting images across social media for four years. The project is part of the North Highland College UHI and the University of the Highlands and Islands. According to The Telegraph, Dr. Alex Bond, one of the researchers from the Natural History Museum in London, called human debris a “global issue.”
They have fielded reports from Sri Lanka, the U.K, Australia, Japan and North America since the start of the pandemic. Bond told the Telegraph that almost all the images they have collected have involved masks. Images depict elastic tangled around bird’s legs or birds injured after trying to consume the mask.
Of the 114 reports, 93% were face masks. Images have shown nine dead animals in direct contact with personal protective equipment, but the fate of most animals is unknown. Since the pandemic, the team has recorded 114 incidents in 23 countries. The paper10 gathered information from social media searches, reports from the citizen science database Birds and Debris, and unpublished reports from colleagues.
The sightings were verified by contacting the observers. The researchers believe that this data underestimates the number of animals that have been harmed by the debris triggered by the pandemic. They went on to write:11
“Widespread use and insufficient infrastructure, combined with improper waste management have resulted in an emerging category of litter. With widespread presence in the environment, such items pose a direct threat to wildlife as animals can interact with them in a series of ways.
It is crucial that we identify opportunities to improve our waste management infrastructure, so that we can prevent similar leakages during the inevitable future pandemics.”
Mindless Masking Raises the Risk of Death and More
It is called “mindless masking” since wearing the mask increases your risk of death, and as we discuss below, there is no scientific evidence that wearing a mask can reduce your risk of getting COVID. German physician Dr. Zacharias Fögen was unable to find published evidence that masking effectively reduced the severity of the disease or had an influence on case fatality.12
He began gathering demographic data from the state of Kansas to analyze the effect of wearing a mask using data in counties where masks were mandated and those that didn’t. The results suggested that masking was not innocuous. In fact, it may present a greater threat than the infection, making it a “debatable epidemiological intervention.”13
The death rate in counties where masks were mandated was 85% higher than in those where they were not. After accounting for confounding factors, the mortality rate remained 52% higher. On further analysis, he wrote, “this study determines that over 95% of this effect can solely be attributed to COVID-19.”14
In other words, while other pathogens or CO2 build-up could have weakened the immune system, it was COVID-19 that caused the rise in deaths in counties where masks were mandated. He named this the Foegen effect, referring to the reinhalation of viral particles trapped in droplets and deposited on the mask, which worsens outcomes.15
Fögen noted two large studies had found similar results with case fatality rates. In other words, the studies found a positive link between masking and death. The first was published in the journal Cureus,16 which found no association between case numbers and mask compliance, but a positive association with death and mask compliance.
The second study17 was published in PLOS One, which revealed an association between negative COVID outcomes and mask mandates across 847,000 people in 69 countries. One report18 focused on the health and safety of wearing masks and proposed the potential of permanent fibrotic lung damage caused by inhaling fibrous nanoparticles. The author explained:19
“There are real and significant dangers of respiratory infection, oral health deterioration and of lung injury, such as pneumothorax, owing to moisture buildup and also exposure to potentially harmful levels of an asphyxiant gas (carbon dioxide [CO2]) which can cause serious injury to health.”
Public Health Officials Ignore Two Years of Data
Jeffrey Anderson, past director of the Bureau of Justice Statistics at the U.S. Department of Justice, makes several salient points after the San Diego, California school board once again took up the mindless mask mandate for school children, decreeing that children who do not wear face coverings would be barred from the classroom.
An August 2022 evaluation of the CDC and Census Bureau figures show that 99.99% of children in California and Florida have not died of COVID — “either because they haven’t gotten it, or because they’ve gotten it and survived it.”20 And yet the two states approached masking completely differently, where California regularly imposed mindless masking and Florida has not. The statistic holds true throughout the U.S.21
Anderson notes that public health experts have thoroughly embraced masking, based on reasoning expounded by Seán Muller that “‘the failure of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to provide supportive evidence’ that masks work to reduce viral transmission.”22,23 Muller goes on to propose that “a statistically significant finding from a high quality RCT (the ‘gold standard’)” should not be the basis for decision making.
Rather “mechanism-based reasoning” should be used that does not require scientific knowledge but rather an application of his own reasoning.24 Muller then argues that “from the perspective of the history of medical science that this logic relies only on a fairly simple germ theory of disease. And it places the burden of proof on those who would argue against recommending face masks.”
In other words, there may not be scientific evidence that mask wearing works, but it makes sense that it does … so if you want to stop wearing masks you must prove they don’t work, and I don’t have to prove that they do work. On the surface, one 2021 study from Bangladesh seems to show that masks do work.
Yet, as Anderson describes,25 after Ben Recht, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the University of California, Berkeley computed the numbers from data the researchers released, they didn’t add up. It turns out that in a group of 178,322 who wore masks and 163,861 who did not, 20 more people without a mask got COVID, which is a 0.08% difference.
The researchers wrote this was “clear evidence that surgical masks lead to a relative reduction in symptomatic seroprevalence of 11.1%.”26 The difference between the two risk percentages is the difference between relative risk reduction and absolute risk reduction. After further analysis of the study, Anderson writes, “these tiny differences register as statistically significant only because of myriad questionable methodological choices.”27
Problems Ignored When Mandating Masks
The mainstream media touted the results as evidence for mask wearing. Yet, as Anderson writes,28further analysis of the data found more interesting figures.
- No statistical significance that masks work under the age of 40
- For people in their 40s, cloth masks work but not surgical masks
- People in their 50s should wear surgical masks and not cloth masks
The researchers distributed red and purple masks to the participants of the study. When Recht analyzed the data, he found “cloth purple masks did nothing, but the red masks ‘work,’” and added, “Indeed, red masks were more effective than surgical masks!” Anderson concludes, “When a study starts producing findings like these, its results start to look like random noise.”29
The fear-mongering prevalent during the mask mandates encouraged people to overlook much of the data and research that challenged the idea that masks might slow the spread of the virus. Some began asking if the masks were effective against the COVID-19 virus, why were they not being treated as a biohazard?30
If there were millions of masks contaminated with SARS-CoV-2, would they not present a danger after being thrown out in the garbage and eventually released into the environment? One preprint study31 posted August 7, 2021, found that mask wearing could:
- Promote facial alkalinization
- Encourage dehydration, which enhances barrier breakdown and raises the risk of bacterial infection
- Increase headaches and sweating
- Decrease cognitive precision, which can lead to medical errors
According to a study32 by Chinese scientists posted in January 2021, wearing a face mask can increase your daily inhalation of microplastics. In April 2022,33 a team of scientists from Hull York Medical School published findings that showed 39 microplastic particles in 11 of 13 lung tissues sampled during lung surgery.
According to the lead scientist, microplastics have been found in autopsies in the past, but this is the first study to demonstrate they are found in the living. Interestingly, these microparticles were also found in the lowest parts of the lungs, which researchers had once thought they could not possibly reach.34
The researchers found the subjects had 12 types of microplastics and the most abundant were polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET).35 This finding points to the recent ubiquitous use of blue surgical masks during the pandemic as PP is the most used plastic component in those masks.
No Benefit Found in COVID-Specific Mask Trial
While multiple studies published before the pandemic demonstrated masks were not effective against viral transfer, U.S. public health experts lobbied hard for mask mandates. This was a driving force in the plastic pollution that has devastated the environment and is injuring and killing wildlife.36 As is portrayed in this short, humorous video, many went along with masking to get along.
Many of the past studies evaluated the efficacy of masking against the flu virus. The first COVID-19-specific randomized controlled surgical mask trial was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine. The data from this study confirmed past findings, showing that:37
- Masks may reduce your risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection by as much as 46%, or they may increase your risk by 23%
- The vast majority — 97.9% of those who didn’t wear masks, and 98.2% of those who did — remained infection free
The conclusions were made on the analysis of data from 4,862 people who completed the study. Among mask wearers, 1.8% tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, compared to 2.1% among controls. When they removed the people who reported not adhering to the recommendations to use masks, the results were the same — 1.8%, which suggests adherence does not make a significant difference.
Among those who reported wearing their face mask “exactly as instructed,” 2% tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 compared to 2.1% of the controls. So, essentially, economies, lives, and the environment have been destroyed to protect a tiny minority from a positive PCR test, which means little to nothing.
Evidence that masks are not effective against viral particles has been published for many years. In addition to the research reviewed above, here’s a sample of what else you’ll find when you start searching for data on face masks as a strategy to prevent viral infection:
- Surgical masks and n95 masks perform about the same — A 2009 study38 published in JAMA compared the effectiveness of surgical masks and N95 respirators against the seasonal flu in a hospital setting; 23.6% of the nurses using surgical masks got the flu and 22.9% of those who wore N95 masks got influenza.
- Cloth masks are far worse than medical masks — A 2015 study39 of healthcare workers showed cloth masks had the highest rate of influenza-like illness and laboratory-confirmed respiratory virus infections when compared to medical masks or controls who used standard practices, including occasional medical masks.
- No significant reduction in flu transmission in a community setting — A policy review paper40in 2020 that reviewed “the evidence base(d) on the effectiveness of nonpharmaceutical personal protective measures … in non-healthcare settings” concluded, based on 10 randomized controlled trials, that there was “no significant reduction in influenza transmission with the use of face masks …”
- Risk reduction may be due to chance — In 2019, a review41 of interventions for flu epidemics published by the World Health Organization concluded the evidence for face masks was slim, and “the evidence was insufficient to exclude chance as an explanation for the reduced risk of transmission.”
- Mask or no mask, same difference — A meta-analysis and scientific review42 led by respected researcher Thomas Jefferson, cofounder of the Cochrane Collaboration, posted on the prepublication server medRxiv in April 2020, found that, compared to no mask, mask wearing in the general population or among health care workers did not reduce influenza-like illness cases or influenza.
*
Note to readers: Please click the share buttons above or below. Follow us on Instagram and Twitter and subscribe to our Telegram Channel. Feel free to repost and share widely Global Research articles.
Notes
1, 4, 9 The Telegraph, August 5, 2022
3, 36 Science of the Total Environment, 2022;848
5 Frontiers of Environmental Science and Engineering, 2021;15(6)
6 European Respiratory Journal, 1994;7(2)
8 Annals of the New York Academy of Science, 2008;1134
10 Science of the Total Environment, 2022;848 Abstract
11 Science of the Total Environment, 2022;848 Abstract and Conclusion last sentence 50% DTP
13 Medicine, 2022;101(7) Abstract para 4
14 Medicine, 2022;101(7) Abstract
17 PLOS|One, 2021, doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0252315
20, 21, 22, 25, 27, 28, 29 City-Journal, August 8, 2022
23 Nature Public Health Emergency Collection, 2021;43(2)
24 Nature Public Health Emergency Collection, 2021;43(2) Numbers in 1st subhead
32 Yahoo News, January 1, 2021
33, 34 Hull York Medical School, April 6, 2022
35 Western Standard, April 17, 2022
37 Annals of Internal Medicine, doi.org/10.7326/M20-6817
40 Emerging Infectious Diseases May 2020; 26(5)
42 medRxiv, 2020; doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.30.20047217
Featured image is from The Weather Network

