Al Qaeda in China, Islamic Insurgency in Uighur-Xinjiang, China and the US-Saudi-Israeli Plan for the Middle East
THE YINON PLAN LIVES ON
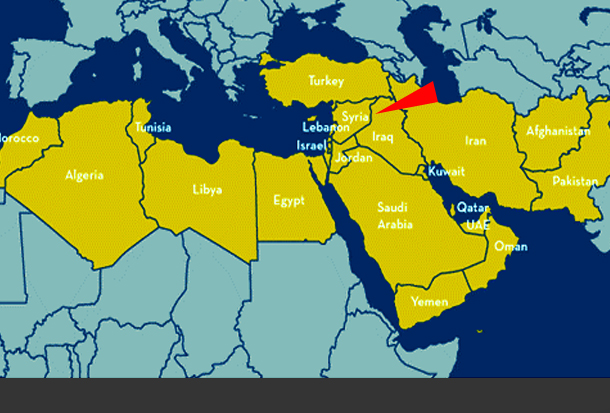
Named after Israel’s minister of foreign affairs at the time of the 1982 invasion of Lebanon and occupation of Beirut, with about 25 000 dead, this divide-and-rule geostrategy plan for the MENA (Middle East and North Africa) lives on.
Already victims of this strategy since 2011 – operated by Israel, the US and Saudi Arabia – we have the divided and weakened states of Iraq, Libya, Yemen and Syria. Egypt and even Tunisia can also possibly be added to the list. Others can be identified as likely short-term target victim countries.
In February 1982 the foreign minister Oded Yinon wrote and published ‘A Strategy for Israel in the Nineteen Eighties‘, which outlined strategies for Israel to become the major regional power in the Middle East. High up the list of his recommendations was to decapitate and dissolve surrounding Arab states into sub-nations, warring between themselves. Called the peace-in-the-feud or simply divide and rule, this was part of Yinon’s strategy for achieving the long-term Zionist goal of extending the borders of Israel, not saying where but potentially a vast region. His strategy was warmly and publicly supported by leading US policy makers with close ties to Israel, like Richard Perle, by the 1990s.
This regional balkanization plan is centred on the exploitation of ethnic, religious, tribal and national divisions within the Arab world. Yinon noted the regional landscape of the MENA was “carved up” mainly by the US, Britain and France after the defeat and collapse of the Ottoman empire in 1917. The hastily traced and arbitrary borders are not faithful to ethnic, religious, and tribal differences between the different peoples in the region – a problem exactly reproduced in Africa, when decolonization started in the 1950s and 1960s. Yinon went on to argue this makes the Arab world a house of cards ready to be pushed over and broken apart into tiny warring states or “chefferies” based on sectarian, ethnic, national, tribal or other divisions.
Central governments would be decapitated and disappear. Power would be held by the warlord chiefs in the new sub-nations or ‘mini-states’. To be sure, this would certainly remove any real opposition to Israel’s coming regional dominance. Yinon said little or nothing about economic “collateral damage”.
To be sure, US and Saudi strategy in the MENA region is claimed to be entirely different, or in the Saudi case similar concerning the means – decapitating central governments – but different concerning the Saudi goal of creating a huge new Caliphate similar to the Ottoman empire. Under the Ottomans nations did not exist, nor their national frontiers, and local governments were weak or very weak.

Al QAEDA: The new US-NATO conscript army in the MENA region, and beyond.
ISLAMIC INSURGENCY IS WELL KNOWN IN CHINA
China knows plenty about Islamic insurgency and its potential to destroy the nation state. Even in the 1980s and 1990s, some 25 years ago, China had an “Islamic insurgency” threat concentrated in its eastern resource-rich and low population Xinjiang region. Before that, since the early days of the Peoples’ Republic in the 1950s, China has addressed Islamic insurgency with mostly failed policies and strategies but more recently a double strategy of domestic or local repression, but aid and support to Islamic powers thought able to work against djihadi insurgents – outside China – has produced results.
The Chinese strategy runs completely against the drift of Western policy and favours Iran.
A report in ‘Asia Times’, 27 February 2007, said this: “Despite al-Qaeda’s efforts to support Muslim insurgents in China, Beijing has succeeded in limiting (its) popular support….. The latest evidence came when China raided a terrorist facility in the country’s Xinjiang region, near the borders with Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and Kirgizstan. According to reports, 18 terrorists were killed and 17 were captured”.
Chinese reporting, even official white papers on defence against terror are notoriously imprecise or simply fabricated. The official line is there is no remaining Islamic insurgency and – if there are isolated incidents – China’s ability to kill or capture militants without social blowback demonstrates the State’s “hearts and minds” policy in Xinjiang, the hearth area for Chinese Muslims, is working.
 Chinese official attitudes to Islamic insurgency are mired with veils of propaganda stretching back to the liberation war against anti-communist forces. These featured the Kuomintang which had a large Muslim contingent in its Kuomintang National Revolutionary Army. The Muslim contingent operated against Mao Zedong’s central government forces – and fought the USSR. Its military insurgency against the central government was focused on the provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia and Xinjiang and continued for as long as 9 years after Mao took power in Beijing, in 1949.
Chinese official attitudes to Islamic insurgency are mired with veils of propaganda stretching back to the liberation war against anti-communist forces. These featured the Kuomintang which had a large Muslim contingent in its Kuomintang National Revolutionary Army. The Muslim contingent operated against Mao Zedong’s central government forces – and fought the USSR. Its military insurgency against the central government was focused on the provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia and Xinjiang and continued for as long as 9 years after Mao took power in Beijing, in 1949.
Adding complexity however, the Muslim armed forces had been especially active against the Soviet Union in the north and west – and by 1959 the Sino-Soviet split was sealed. Armed hostilities by Mao’s PLA against the Red Army of the USSR broke out in several border regions, with PLA forces aided by former Muslim insurgents in some theatres. Outside China, and especially for Arab opinion, Mao was confirmed as a revolutionary nationalist similar to non-aligned Arab leaders of the period, like Colonel Husni al-Zaim of Syria and Colonel Nasser of Egypt.
CHINA’S THREAT TO WESTERN STRATEGY IN THE MENA
Especially today, some Western observers feign “surprise” at China’s total hostility towards UN Security Council approval for “surgical war” strikes against Syria. The reasons for this overlap with Russia’s adamant refusal to go along with US, Saudi Arabian, Turkish and French demands for a UNSC rubber stamp to trigger “regime change” in Syria but are not the same. For China the concept of “regime change” with no clear idea – officially – of what comes next is anathema.
As we know, when or if al Assad falls, only chaos can ensue as the country breaks apart, but this nightmare scenario for China is brushed aside by Western politicians as a subject for “later decision”.
China’s successful efforts to keep the global jihad from spreading into its territory is surely and certainly taken as a real challenge by Saudi-backed insurgents in western China. Various reports indicate the al-Qaeda organization trains about 1 000 mostly Xinjiang-origin Uighurs and other Chinese Muslims every year. Located in camps in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Kirgizstan and elsewhere, this terror training has continued since at least the mid-1990s, for a total of more than 15 years.
The focus on Xinjiang, formerly called Turkestan is no accident. The region’s Russian influence is still strong, reinforced by Muslim migration from Russia in the 19th century, accelerated by the Russian Civil War and 1917 revolution. During China’s warlord era preceding Mao’s rule, the USSR armed and supported the Muslim separatist East Turkestan Republic which only accepted Mao’s rule when the PRC under the Chinese communists was fully established in 1949. The longstanding East Turkestan jihadi movement (ETIM) is highly active today after being relaunched in the early 2000′s, especially since the Iraq war of 2003. It however mainly acts in “external theatres” such as Pakistan’s Baluchistan province. The Baluchi of Pakistan have long-term rebellious relations with the central government in Islamabad, and are allied with Kurd nationalists in Iraq, Syria, Lebanon and Turkey.
The US Council on Foreign Relations in a 29 May 2012 briefing on Xinjiang noted that since the Chinese Qing dynasty collapse of 1912, the region has experienced various types of semi-autonomy and on several occasions declared full independence from China. The Council for example notes that in 1944, factions within Xinjiang declared independence with full support from the USSR, but then cites US State Dept. documents claiming that Uighur-related terrorism has “declined considerably” since the end of the 1990s and China “overreacts to and exaggerates” Islamic insurgency in Xinjiang.
Notably, the US has declassified the ETIM Islamic movement – despite its terror attacks – as a terrorist organization. The ETIM was defined as such during the Bush administration years, but is no longer listed as a Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) in the State Dept. FTO list as from January 2012.
China has fully recognized the Islamic insurgency threat, with its potential for drawing in hostile foreign powers seeking to destroy national unity and break the national government. Its concern, shared by Indian strategists and policy makers is to “stop the rot” in the MENA.
Unofficially, China regards the US and Saudi strategy in the MENA and Central Asia as “devil’s work” sowing the seeds of long-term insurgency, the collapse of the nation state and with it the economy. The US link with and support to Israel is in no way ignored, notably Israel’s Yinon plan for weakening central governments and dissolving the nation state right across the MENA.
China’s main concern is that Central Asian states will be affected, or infected by radical Islamic jihadi fighters and insurgents drifting in from the West, from the Middle East and North Africa. These will back the existing Islamic insurgent and separatist movement in resource-rich Xinjiang. To keep Central Asian states from fomenting trouble in Xinjiang, China has cultivated close diplomatic ties with its neighbors, notably through the Shanghai Cooperation Organization which has a secretariat concerned with counter-insurgency issues.
US analysts however conclude, very hastily, that China “instinctively supports the status quo” and therefore does not have an active international strategy to combat djihadi violence and anarchy outside China. US analysts say, without any logic, that China will respond to and obediently follow initiatives from Washington and other Western powers – as it has starkly not done in the UN Security Council when it concerns the Western powers’ long drawn out attempt to repeat, for Syria, their success in 2011 for getting UNSC approval to the NATO war in Libya!
China was enraged, and regarded it as betrayal when its support for limited action by NATO in Libya – a rare instance of China compromising on nonintervention – turned into an all-out “turkey shoot” to destroy the Gaddafi clan. Libya was handed over to djihadi militants, who subsequently declared war against central government, an accelerating process resulting in Libya, today, having no central government with any real authority. That experience certainly hardened Beijing’s responses on Syria.
Post-Mao China has restored the concept of Chinese cultural continuity, with a blend of Confucian, Taoist and Buddhist strands which had been been weakened but not completely destroyed in the years of ideologically-driven Communism. For the Communists of Mao’s era “history was bunk”, not even a mixed bag but an unqualified evil that must be smashed. The Chinese attitude to radical Islam as embodied in the ideologies of Wahabism and Salafism is the same – they are treated as a denial of world history and its varied cultures, with immediate and real dangers for China. Its counter-insurgency strategy against Islamic radicals is the logical result.
This strategy ensures closer Tehran-Beijing relations, usually described by Western analysts as a “balancing act” between ties to Washington and growing relations with Iran. China and Iran have developed a broad and deep partnership centered on China’s oil needs, to be sure, but also including significant non-energy economic ties, arms sales, defense cooperation, and Asian and MENA geostrategic balancing as a counterweight to the policies and strategies of the United States and its local allies, Saudi Arabia and Israel. Chinese attention now focuses the Washington-Riyadh axis and its confused and dangerous MENA region geostrategy, resulting in a de facto proliferation of Islamic djihadi insurgents and the attack on the basic concept of the nation state across the region. The Chinese view is that Iran’s version of “Peoples’ Islam” is less violent and anarchic, than the Saudi version.
OPPOSING THE WASHINGTON-RIYADH AXIS
Both Chinese and Indian strategists’ perceptions of the US-Saudi strategy in the MENA, and other Muslim-majority regions and countries is that it is dangerous and irresponsible. Why the Western democracies led by the US would support or even tolerate the Saudi geostrategy and ignore Israel’s Yinon Plan – as presently shown in Syria – is treated by them as almost incomprehensible.
China is Tehran’s largest trading partner and customer for oil exports, taking about 20% of Iran’s total oil exports, but China’s co-operation is seen as critical to the Western, Israeli and Arab Gulf State plan to force Iran to stop uranium enrichment and disable the capacity of its nuclear program to produce nuclear weapons. Repeated high-level attempts to “persuade Beijing” to go along with this plan, such as then-US Treasury Secretary Timothy Geithner’s 2012 visit to Beijing, however result each time in Chinese hosts politely but firmly saying no. This is not only motivated by oil supply issues.
Flashpoints revealing the Chinese-US divide on Iran crop up in world news, for example the US unilateral decision in January 2012 to impose sanction on Chinese refiner Zhuhai Zenrong for refining Iranian oil and supplying refined products back to Iran. This US action was described by China’s Foreign Ministry spokesman as “totally unreasonable”. He went on to say that “China (has) expressed its strong dissatisfaction and adamant opposition”.
At the same time, China’s Xinhua Agency gave prominence to the statement made by Iran’s OPEC delegate Mohamed Ali Khatibi: “If the oil producing nations of the (Arab) Gulf decide to substitute Iran’s oil, then they will be held responsible for what happens”. Chinese analysts explained that China like India was irritated that Iranian oil sanctions opened the way for further de facto dominance of Saudi Arabia in world export supplies of oil, as well as higher prices.
Iran is however only the third-largest supplier of oil to China, after Angola and Saudi Arabia, with Russia its fourth-largest supplier, using EIA data. This makes it necessary for China to run sustainable relations with the Wahabite Kingdom, which are made sustainable by actions like China’s Sinopec in 2012 part-funding the $8.5 billion 400 000 barrels-per-day refinery under construction in the Saudi Red Sea port city of Yanbu.
The Saudi news and propaganda outlet Al Arabiya repeatedly criticises China and India for their purchase of Iranian oil and refusal to fully apply US-inspired sanctions. A typical broadside of February 2013 was titled “Why is China still dealing with Iran?”, and notably cited US analysts operating in Saudi-funded or aided policy institutes, such as Washington’s Institute for Near East Policy as saying: “It’s time we wised up to this dangerous game. From Beijing’s perspective, Iran serves as an important strategic partner and point of leverage against the United States”. US analysts favourable to the Saudi strategy in the MENA – described with approval by President Eisenhower in the 1950s as able to establish a Hollywood style Saudi royal “Islamic Pope” for Muslim lands from Spain to Indonesia – say that Iran is also seen by China as a geopolitical partner able to help China countering US-Saudi and Israeli strategic action in the Middle East.
A 2012 study by US think tank RAND put it bluntly: “Isolated Iran locked in conflict with the United States provides China with a unique opportunity to expand its influence in the Middle East and could pull down the US military in the Gulf.” The RAND study noted that in the past two decades, Chinese engineers have built housing, bridges, dams, tunnels, railroads, pipelines, steelworks and power plants throughout Iran. The Tehran metro system completed between 2000 and 2006 was a major Chinese engineering project.
THE BIG PICTURE
China’s Iran policy and strategy can be called “big picture”. Iranian aid and support to mostly but not exclusively Shia political movements, and insurgents stretches from SE Asia and South Asia, to West and Central Asia, Afghanistan, the Caspian region, and SE Europe to the MENA. It is however focused on the Arabian peninsula and is inevitably opposed to Saudi geostrategy. This is a known flashpoint and is able to literally trigger a third world war. Avoiding this is the big picture – for China.
Li Weijian, the director of the Research Center of Asian and African Studies at the Shanghai Institute for International Studies puts it so: “China’s stance on the Iranian nuclear issue is not subject to Beijing’s demand for Iranian oil imports, but based on judgment of the whole picture.” China is guided in foreign relations by two basic principles, both of them reflecting domestic priorities. First, China wants a stable international environment so it can pursue domestic economic development without external shocks. Second, China is very sensitive to international policies that ‘interfere in or hamper sovereign decisions”, ultimately tracing to its experience in the 19th and 20th centuries at the hands of Western powers, and the USSR, before and after the emergence of the PRC. It adamantly opposes foreign interference in Taiwan, Tibet, and Xinjiang.
This includes radical Islamist or djihadi interference, backed by any foreign power. While China has on occasions suspected Tehran of stirring Islamic insurgency inside its borders it sees the US-Saudi geostrategy of employing djihadists to do their dirty work as a critical danger, and as wanton interference. Indian attitudes although not yet so firm, are evolving in the same general direction. Both are nuclear weapons powers with massive land armies and more than able to defend themselves.
Claims by Western, mostly US analysts that China views Iran as exhibiting “unpredictable behaviour” in response to US-led sanctions and that Iran is “challenging China’s relations with its regional partners” can be dismissed. In particular and concerning oil, China is well aware that Iran will need many years of oil-sector development to return to anything like pre-Islamic revolution output of more than 5 million barrels a day. Unless oil sanctions are lifted, Iran’s oil output will go on declining, further increasing the power of the Gulf States led by Saudi Arabia, and Shia-governed but insurgency threatened Iraq to dictate export prices.
China dismisses the claim that its policies have hampered US and other Western political effort to dissuade Iran from developing nuclear weapons capability.
China’s distaste for toppling almost any central government, even those run by dictatorial strongmen springs from a deep sense of history – marked by insecurity about the uncertain political legitimacy of governments arising from civil war and revolution – like the PRC. At its extreme, this Chinese nightmare extends to fears that if the US-Saudi geostrategy can topple governments in the Middle East almost overnight, what will stop them from working to bring down China’s government one day? Unlike almost all MENA countries minus the oil exporters, China has scored impressive victories in the fight against poverty. Its economy although slowing creates abundant jobs and opportunity.
For China, this is the only way to progress.
HARDENING POLICIES AND POSITIONS
The emerging Chinese anti-Islamist strategy also underlines a menacing reality for the US and other Western powers. China rejects the belief there is still only one superpower in today’s world—the USA. The USA’s weakened economy and uncontrollable national debt, its confused and cowardly drone war, its slavish support to Israeli and Saudi whims do not impress China – or India.
To be sure China’s classic-conventional weapons development programs lag far behind the US. The Chinese military strategy for pushing back US dominance focuses global reach ballistic missiles, tactical nuclear weapons, drones, submarines, and military space and cyberwarfare capabilities.
With the PLA it possesses the biggest land army in the world. No US warmonger, at least saner versions would “take on China”.
China has invested heavily in Iraq, Saudi Arabia and other Gulf states, as well as Iran. It does not want to see its investment effort destroyed by deliberately promoted Islamic anarchy. Also, its Middle Eastern presence will continue due to the fact that while US dependence on oil imports is declining, China overtook the US as the world’s largest oil importer on a daily basis, this year, several years ahead of analysts’ consensus forecasts.
The likely result is that China is now poised and almost certain to strengthen relations with Iran. The intensifying Syrian crisis as well as the dangerously out of control US-Saudi-Israeli djihadi strategy, of fomenting sectarian conflict and destroying the nation state in the MENA, will likely prompt China to soon take major initiatives.